尊龙凯时网娱乐官网的产品展示navigation

电话:021-35183767
021-35183767
传真:021-35183767-8008
qq:2881513768
地址:上海市闵行区兴梅路485号 xingmei rd 485shanghaichina
ugo basile电子测痛仪
时间:2023-12-22来源:本站作者:玉研仪器

详细介绍
机械感觉灵敏度阈值检测,用于镇痛药物、伤害性疼痛、神经病理学、术后疼痛等研究过程中的感觉过敏和痛觉超敏评估。
von frey纤维丝是临床及临床前科研领域,神经病理学疼痛行为评估的传统方法,但其测试过程繁琐且乏味,实验人员不易掌握计算方法,容易出错。
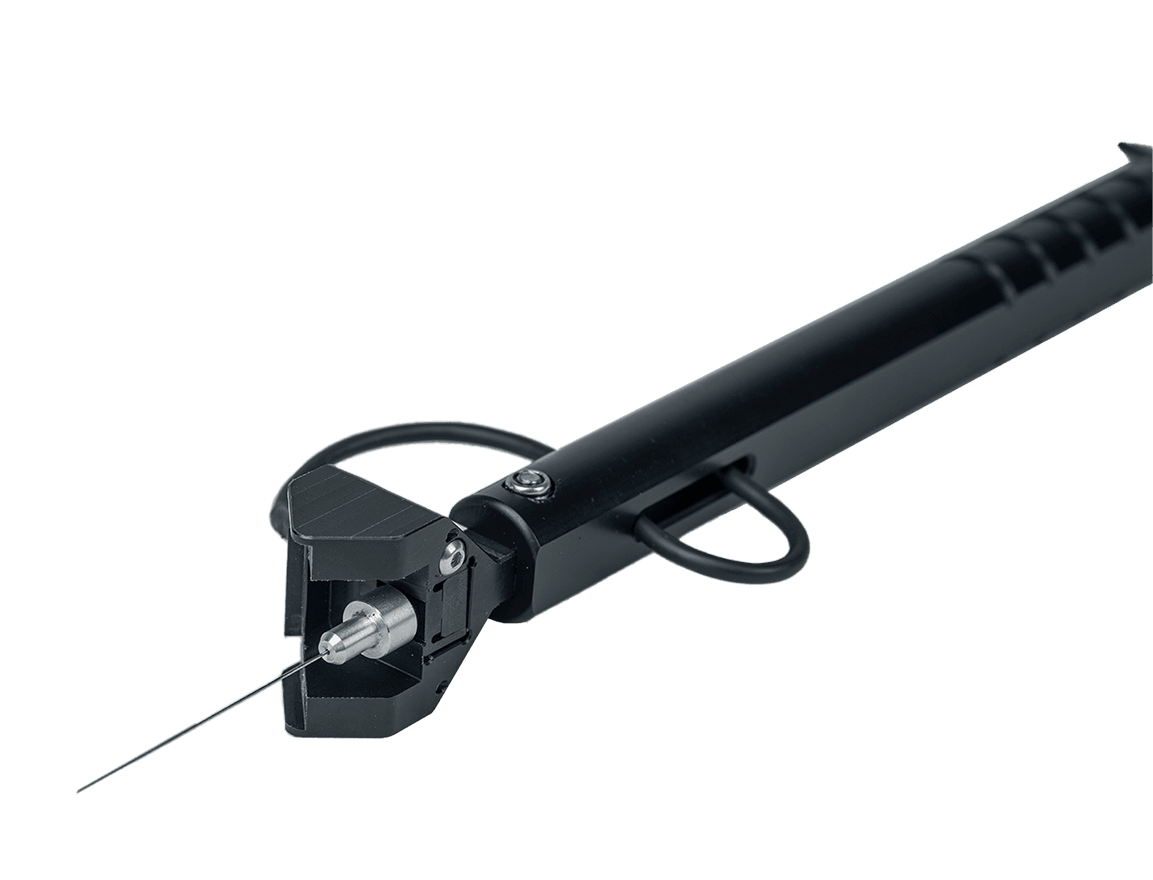
ugo basile电子测痛仪(100%痛阈评估法)是针对机械刺激中的针刺痛觉,评估大小鼠机械痛阈的先进方法。相较于von frey纤维丝每根丝施加力为固定值,电子测痛仪可以施加从小至大连续的力,提供了在连续尺度上鼠爪缩回疼痛阈值的精确测量。设备采用手持式力传感器及固定硬性测试头设计,搭配软件固定施力曲线可得到稳定的测试结果,有效降低了测试工作量和实验者偏差。
测试时,将动物放置在测试平台上,通过手持式力传感器动物对足底逐渐施加压力,直到动物动物出现缩足、舔足、跳跃反应,仪器自动记录(或手动)压力峰值和峰值出现时间点。
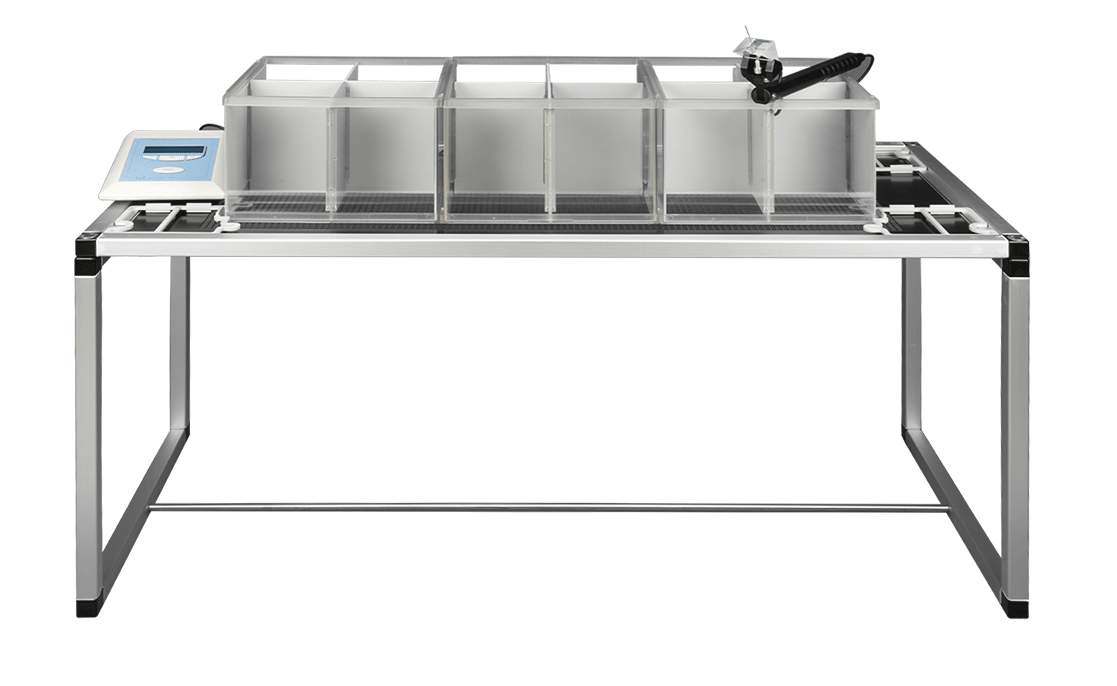
优势特点:
一、可控制垂直施压
在机械痛阈值评估过程中,压力方向需要与受力面垂直以减小矢量对于实验影响,电子测痛仪人体工学设计可方便轻松控制金属针在施力过程中与鼠足足底垂直。
二、可精准定位刺痛位点
ugo basile 电子测痛仪的另一特点是具有一个三棱镜,通过光学折射,可迅速定位金属针尖的位置,对于精确定位测试位点非常重要。
三、自动校准与记录
ugo basile 电子测痛仪的易用性不仅体现在疼痛阈值测试方案的简化,当痛阈出现,仪器自动记录压力峰值出现的时间和大小,同时具有自动校准功能,长期使用时也可保持数据准确性,无需担心校准问题。
四、3种量程范围可选,存储容量大
为保证其精度,可根据具体疼痛模型,选择0-50g、0-200g、0-1500g施力量程。设备可实时记录测试结果并保存,存储容量高达数百个。
五、可设定施力斜率,施力曲线可直观比较
ugo basile 电子测痛仪具有自定义线性增力范围设置,可根据不同模型设置相应的施力斜率,最大限度提升线性增力的稳定情况。通过将恒定的斜率视为参考值,实验人员在施力时尝试匹配设定线性增力的直线,可提高实验结果准确度与一致性。



电子测痛仪可用于各种神经损伤的神经病变应用,从部分坐骨神经结扎(pnl),到慢性压迫性损伤(cci)和脊髓神经结扎(snl)等,用于评估模型建立和药物治疗过程中的痛觉异常和感觉过敏。

| 38450 | 电子测痛仪完整套装,包含主机、传感器手柄、脚踏板、软件等 |
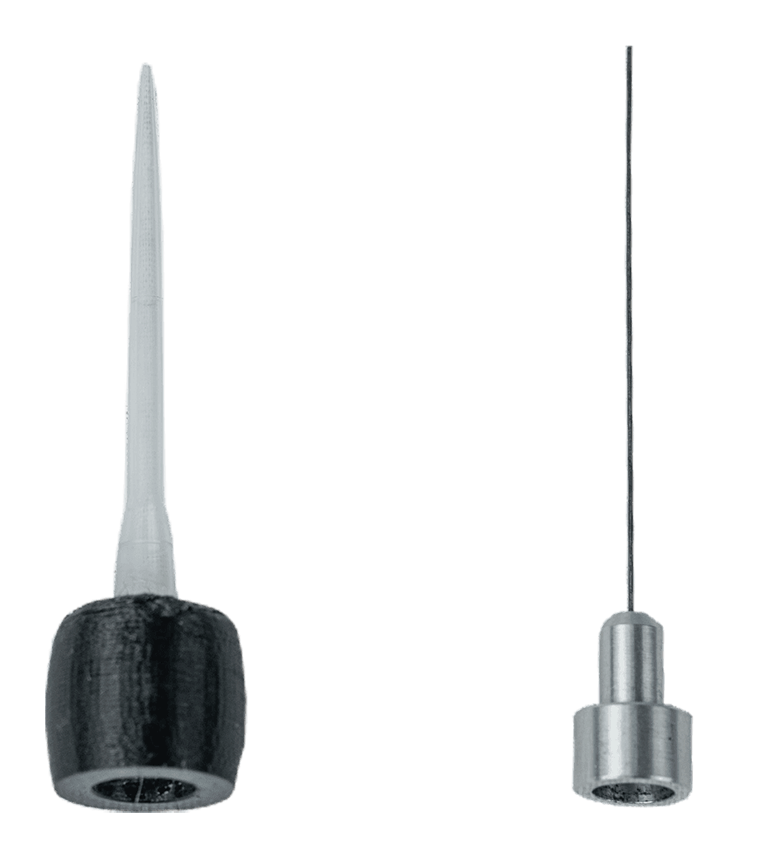
| 38450-331 | 塑料测试头(选配) |
| 37450-278 | 网状动物测试平台,包含支架及动物活动隔间(选配) |
参考文献:
1.liu, zhi-yuan et al. “cxcl12/cxcr4 signaling contributes to neuropathic pain via central sensitization mechanisms in a rat spinal nerve ligation model.” cns neuroscience & therapeutics vol. 25,9 (2019): 922-936. doi:10.1111/cns.13128
2.wu, wenyao et al. “pharmacological inhibition of the cgas-sting signaling pathway suppresses microglial m1-polarization in the spinal cord and attenuates neuropathic pain.” neuropharmacology vol. 217 (2022): 109206. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109206
3.liu, bao-wen et al. “ngf-induced nav1.7 upregulation contributes to chronic post-surgical pain by activating sgk1-dependent nedd4-2 phosphorylation.” molecular neurobiology vol. 58,3 (2021): 964-982. doi:10.1007/s12035-020-02156-1
4.hong, yishun et al. “angiotensin ii type 1 receptor blockade attenuates posttraumatic stress disorder-related chronic pain by inhibiting glial activation in the spinal cord.” neuropharmacology vol. 196 (2021): 108704. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108704
5.sharfman, nathan m et al. “melanocortin-4 receptor signaling in the central amygdala mediates chronic inflammatory pain effects on nociception.” neuropharmacology vol. 210 (2022): 109032. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109032
6.kim, kyeongmin et al. “insular cortex stimulation alleviates neuropathic pain via erk phosphorylation in neurons.” cns neuroscience & therapeutics, 10.1111/cns.14126. 20 feb. 2023, doi:10.1111/cns.14126
7.choi, songyeon et al. “modulation of neuropathic pain by glial regulation in the insular cortex of rats.” frontiers in molecular neuroscience vol. 15 815945. 13 apr. 2022, doi:10.3389/fnmol.2022.815945
8.cha, myeounghoon et al. “diffusion tensor imaging reveals sex differences in pain sensitivity of rats.” frontiers in molecular neuroscience vol. 16 1073963. 2 mar. 2023, doi:10.3389/fnmol.2023.1073963
9.zhang, run et al. “spinal microglia-derived tnf promotes the astrocytic jnk/cxcl1 pathway activation in a mouse model of burn pain.” brain, behavior, and immunity vol. 102 (2022): 23-39. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2022.02.006
10.jiang, shan et al. “itch-specific neurons in the ventrolateral orbital cortex selectively modulate the itch processing.” science advances vol. 8,30 (2022): eabn4408. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abn4408
11.bazan, hernan a et al. “a novel pipeline of 2-(benzenesulfonamide)-n-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acetamide analgesics that lack hepatotoxicity and retain antipyresis.” european journal of medicinal chemistry vol. 202 (2020): 112600. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112600
12.xu, biao et al. “nav1.7 channel blocker [ala5, phe6, leu26, arg28]gptx-1 attenuates cfa-induced inflammatory hypersensitivity in rats via endogenous enkephalin mechanism.” the journal of pain, s1526-5900(22)00481-3. 29 dec. 2022, doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.12.012
您想了解更多详细资料吗?
请与我们联系:
tel:021-35183767,021-54377179
18502129044
qq:3007536621
微信:yuyanbio
mail:yuyanbio@126.com
欢迎您的咨询
