取消
清空记录
历史记录
清空记录
历史记录


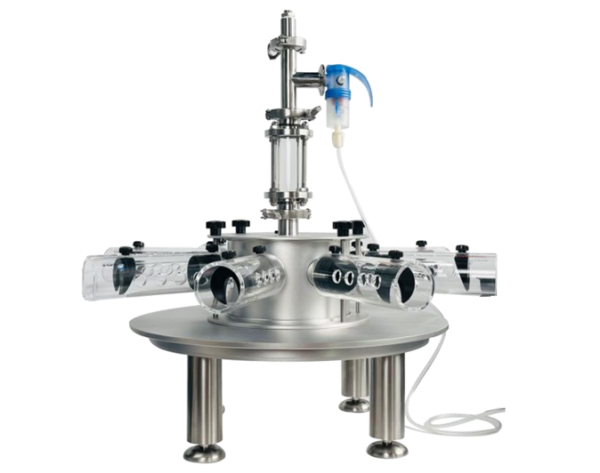
鼠爪肿胀测量仪-尊龙凯时网娱乐官网
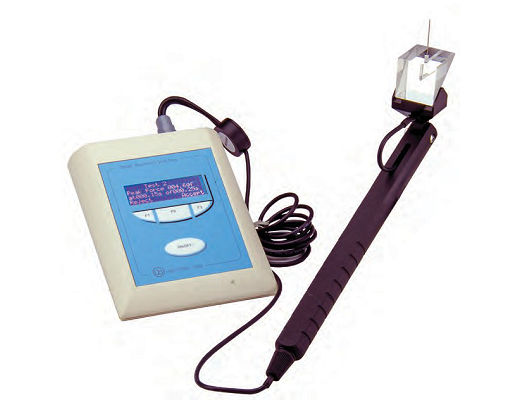
通过测量动物鼠爪体积和水肿(组织液病理性滞留)的微小变化,以衡量炎症反应程度,用于药物筛选试验。 设备具有0.01ml体积分辨率,精确测量啮齿动物爪子体积的变化。
在各类因素引起的四肢关节炎、水肿的发生机制及通过药物改善其炎症的药理学研究中,量化大小鼠四肢的肿胀表征改变情况已被证明具有重要价值。
ugo basile 鼠爪肿胀测量仪通过体积描记器记录排水量来测量大小鼠四肢炎症导致的体积微小变化。20 世纪60年代,ugo basile开发了一个原始设备,专门用于测量啮齿类动物的爪子肿胀,至今为止,数千名科学家依靠这款经典的鼠爪肿胀仪进行炎症研究,发表了近 3000 篇科学论文!
使用时,将导电溶液注入蓄水池,蓄水池通过管路将溶液输送至体积描记传感室和鼠爪水池(两者底部相通)。将具有炎症或水肿模型的鼠爪放入鼠爪水池,体积描记传感器记录溶液体积变化;对动物进行消*处理,再次记录溶液体积变化,便可得出药物效果。
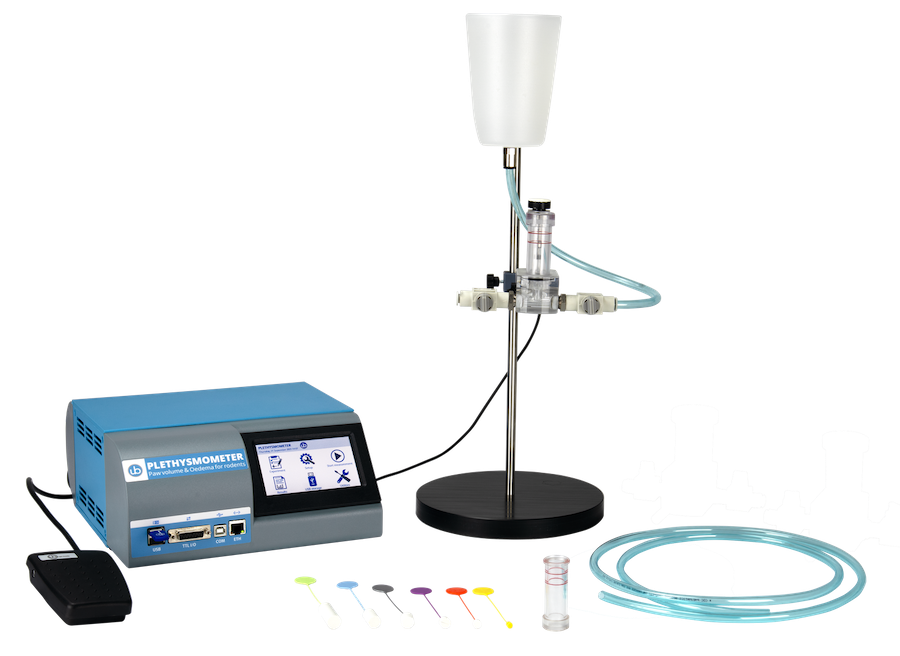

优势特点:
1.药物抗*活性筛选直接的测试工具
传统的机械痛和冷热痛类设备可以很好的进行药物镇痛效果评价,但无法直接验证药物抗*消肿活性。鼠爪肿胀测量仪可对动物各类炎症及疼痛模型中诱肿及消肿引起的体积变化进行直接测量,是经典的药物抗*活性筛选方法。
2.校准方便、快捷
校准前只需按下主机触摸屏清零键,然后把校准组件放入鼠爪水池,数值稳定后,按下确定键后便可开始实验,整个过程只需数分钟。多个校准组件可自由选择,单次校准即可完成。
校准组件有(ml):0.1、0.2、0.5、1、2、4
3.精确测量、自动记录、数据一键导出
0.01ml高分辨率、集成的精密传感器传感器可监测到微弱的体积变化,主机触摸屏实时显示并记录读数,脚踏板开关冻结目标数值不再变化。测试完成后,可通过u盘一键导出csv格式数据表格。
4.多种规格鼠爪池可选,适用范围广
除了标准配置的1.8cm和1.3cm直径的大小鼠爪池,研究人员可根据特殊的实验类型和方案选择肥胖大鼠和豚鼠适用的鼠爪池及适配器。
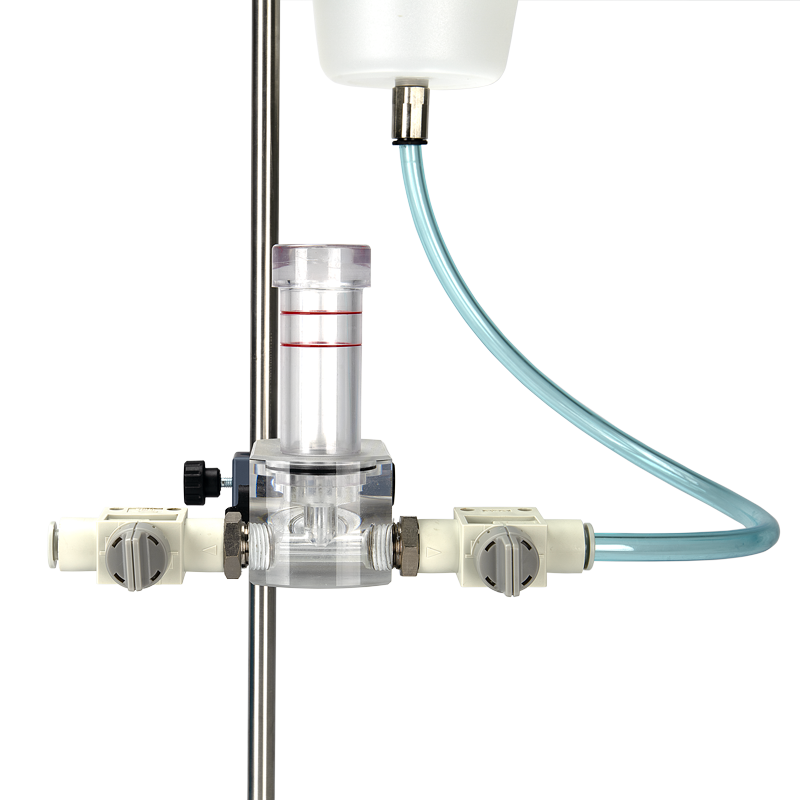
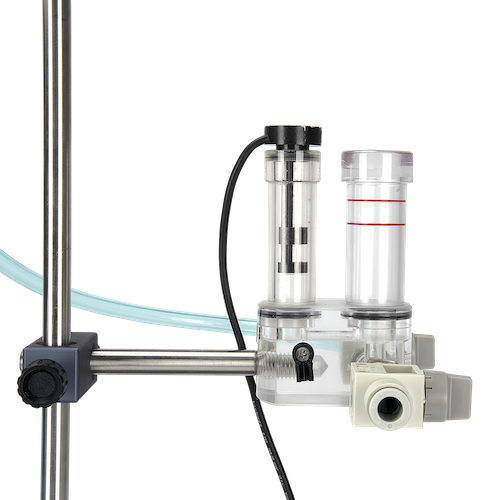
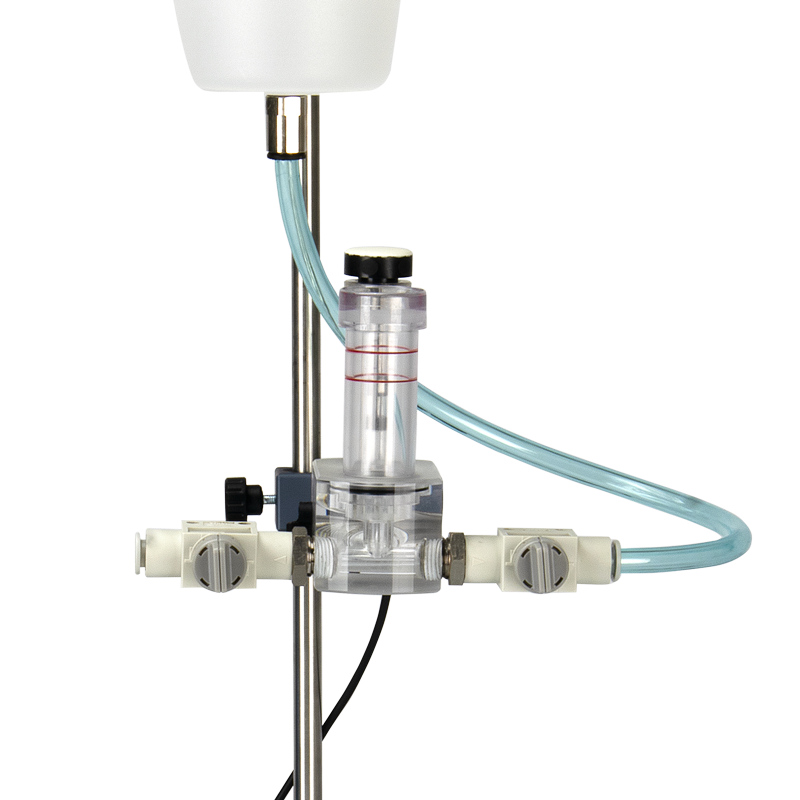
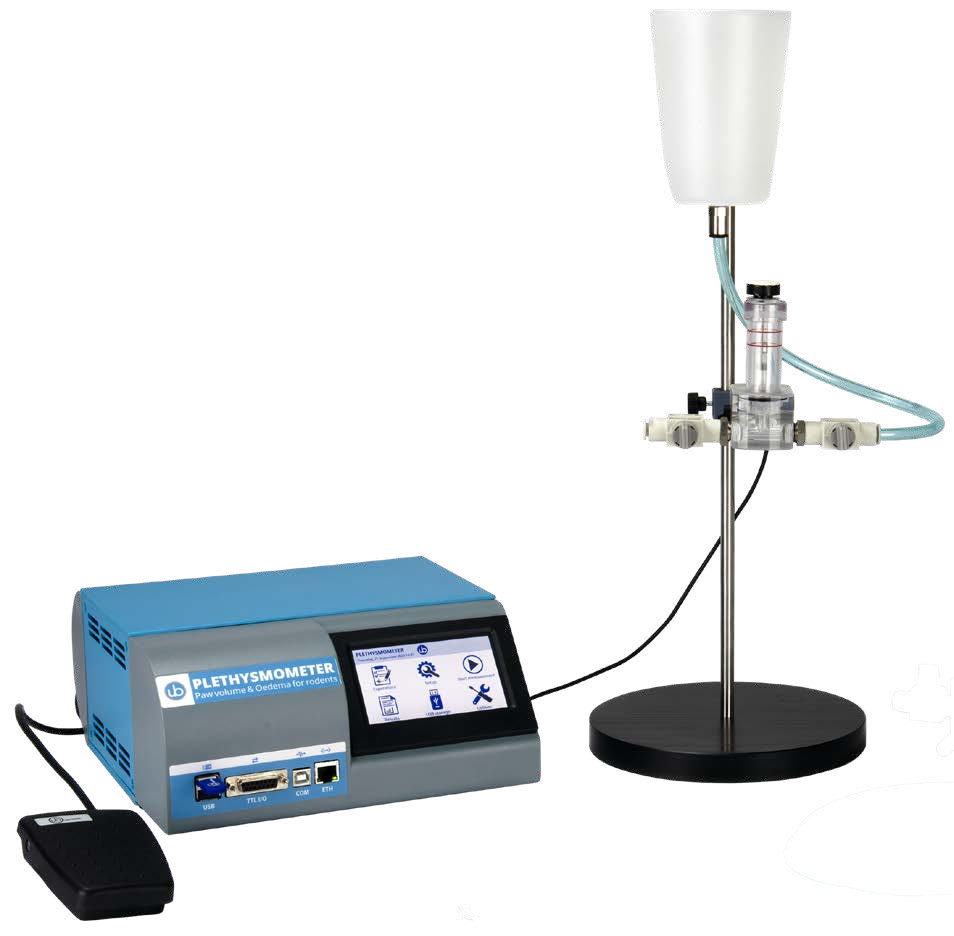
应用领域:
鼠爪肿胀测量仪用于炎症的发展机制研究,对各类已有和潜在药物的消*、抗*效果进行评价和筛选,为药物抗*效果评价类设备。

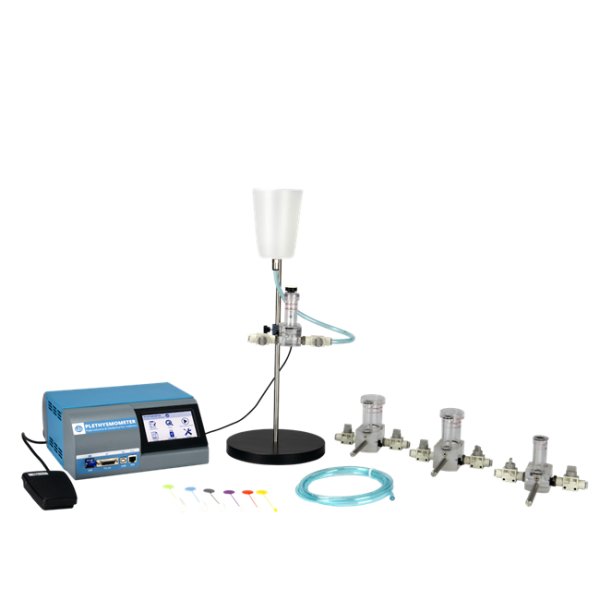
型号规格:
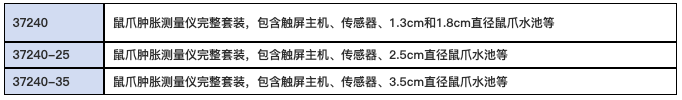
参考文献:
1. chen, yong, et al. "epithelia-sensory neuron cross talk underlies cholestatic itch induced by lysophosphatidylcholine." gastroenterology 161.1 (2021): 301-317. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.049
2. zhang, run, et al. "spinal microglia-derived tnf promotes the astrocytic jnk/cxcl1 pathway activation in a mouse model of burn pain." brain, behavior, and immunity 102 (2022): 23-39. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2022.02.006
3. shlomy, iftach, et al. "restoring tactile sensation using a triboelectric nanogenerator." acs nano 15.7 (2021): 11087-11098. doi:10.1021/acsnano.0c10141
4. jiang, shan, et al. "itch-specific neurons in the ventrolateral orbital cortex selectively modulate the itch processing." science advances 8.30 (2022): eabn4408. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn4408
5. zabala, alazne, et al. "p2x4 receptor controls microglia activation and favors remyelination in autoimmune encephalitis." embo molecular medicine 10.8 (2018): e8743. doi:10.15252/emmm.201708743
6. velichkova, atanaska n., sophie e. coleman, and carole torsney. "postoperative pain facilitates rat c-fibre activity-dependent slowing and induces thermal hypersensitivity in a sex-dependent manner." british journal of anaesthesia 128.4 (2022): 718-733. doi:10.1016/j.bja.2021.10.053
7. zhang, ting, et al. "preemptive intrathecal administration of endomorphins relieves inflammatory pain in male mice via inhibition of p38 mapk signaling and regulation of inflammatory cytokines." journal of neuroinflammation 15 (2018): 1-14. doi:10.1186/s12974-018-1358-3
8. joksimovic, sonja l., et al. "selective inhibition of cav3. 2 channels reverses hyperexcitability of peripheral nociceptors and alleviates postsurgical pain." science signaling 11.545 (2018): eaao4425. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aao4425
9. joksimovic, sonja lj, et al. "novel neuroactive steroid with hypnotic and t‐type calcium channel blocking properties exerts effective analgesia in a rodent model of post‐surgical pain." british journal of pharmacology 177.8 (2020): 1735-1753. doi:10.1111/bph.14930
10. zhang, wenxin, et al. "estrogen modulation of pain perception with a novel 17β-estradiol pretreatment regime in ovariectomized rats." biology of sex differences 11 (2020): 1-13. doi:10.1186/s13293-019-0271-5

通过测量动物鼠爪体积和水肿(组织液病理性滞留)的微小变化,以衡量炎症反应程度,用于药物筛选试验。 设备具有0.01ml体积分辨率,精确测量啮齿动物爪子体积的变化。
在各类因素引起的四肢关节炎、水肿的发生机制及通过药物改善其炎症的药理学研究中,量化大小鼠四肢的肿胀表征改变情况已被证明具有重要价值。
ugo basile 鼠爪肿胀测量仪通过体积描记器记录排水量来测量大小鼠四肢炎症导致的体积微小变化。20 世纪60年代,ugo basile开发了一个原始设备,专门用于测量啮齿类动物的爪子肿胀,至今为止,数千名科学家依靠这款经典的鼠爪肿胀仪进行炎症研究,发表了近 3000 篇科学论文!
使用时,将导电溶液注入蓄水池,蓄水池通过管路将溶液输送至体积描记传感室和鼠爪水池(两者底部相通)。将具有炎症或水肿模型的鼠爪放入鼠爪水池,体积描记传感器记录溶液体积变化;对动物进行消*处理,再次记录溶液体积变化,便可得出药物效果。

优势特点:
1.药物抗*活性筛选直接的测试工具
传统的机械痛和冷热痛类设备可以很好的进行药物镇痛效果评价,但无法直接验证药物抗*消肿活性。鼠爪肿胀测量仪可对动物各类炎症及疼痛模型中诱肿及消肿引起的体积变化进行直接测量,是经典的药物抗*活性筛选方法。
2.校准方便、快捷
校准前只需按下主机触摸屏清零键,然后把校准组件放入鼠爪水池,数值稳定后,按下确定键后便可开始实验,整个过程只需数分钟。多个校准组件可自由选择,单次校准即可完成。
校准组件有(ml):0.1、0.2、0.5、1、2、4
3.精确测量、自动记录、数据一键导出
0.01ml高分辨率、集成的精密传感器传感器可监测到微弱的体积变化,主机触摸屏实时显示并记录读数,脚踏板开关冻结目标数值不再变化。测试完成后,可通过u盘一键导出csv格式数据表格。
4.多种规格鼠爪池可选,适用范围广
除了标准配置的1.8cm和1.3cm直径的大小鼠爪池,研究人员可根据特殊的实验类型和方案选择肥胖大鼠和豚鼠适用的鼠爪池及适配器。



应用领域:
鼠爪肿胀测量仪用于炎症的发展机制研究,对各类已有和潜在药物的消*、抗*效果进行评价和筛选,为药物抗*效果评价类设备。

型号规格:

参考文献:
1. chen, yong, et al. "epithelia-sensory neuron cross talk underlies cholestatic itch induced by lysophosphatidylcholine." gastroenterology 161.1 (2021): 301-317. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.049
2. zhang, run, et al. "spinal microglia-derived tnf promotes the astrocytic jnk/cxcl1 pathway activation in a mouse model of burn pain." brain, behavior, and immunity 102 (2022): 23-39. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2022.02.006
3. shlomy, iftach, et al. "restoring tactile sensation using a triboelectric nanogenerator." acs nano 15.7 (2021): 11087-11098. doi:10.1021/acsnano.0c10141
4. jiang, shan, et al. "itch-specific neurons in the ventrolateral orbital cortex selectively modulate the itch processing." science advances 8.30 (2022): eabn4408. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn4408
5. zabala, alazne, et al. "p2x4 receptor controls microglia activation and favors remyelination in autoimmune encephalitis." embo molecular medicine 10.8 (2018): e8743. doi:10.15252/emmm.201708743
6. velichkova, atanaska n., sophie e. coleman, and carole torsney. "postoperative pain facilitates rat c-fibre activity-dependent slowing and induces thermal hypersensitivity in a sex-dependent manner." british journal of anaesthesia 128.4 (2022): 718-733. doi:10.1016/j.bja.2021.10.053
7. zhang, ting, et al. "preemptive intrathecal administration of endomorphins relieves inflammatory pain in male mice via inhibition of p38 mapk signaling and regulation of inflammatory cytokines." journal of neuroinflammation 15 (2018): 1-14. doi:10.1186/s12974-018-1358-3
8. joksimovic, sonja l., et al. "selective inhibition of cav3. 2 channels reverses hyperexcitability of peripheral nociceptors and alleviates postsurgical pain." science signaling 11.545 (2018): eaao4425. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aao4425
9. joksimovic, sonja lj, et al. "novel neuroactive steroid with hypnotic and t‐type calcium channel blocking properties exerts effective analgesia in a rodent model of post‐surgical pain." british journal of pharmacology 177.8 (2020): 1735-1753. doi:10.1111/bph.14930
10. zhang, wenxin, et al. "estrogen modulation of pain perception with a novel 17β-estradiol pretreatment regime in ovariectomized rats." biology of sex differences 11 (2020): 1-13. doi:10.1186/s13293-019-0271-5
 浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~
浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~