取消
清空记录
历史记录
清空记录
历史记录


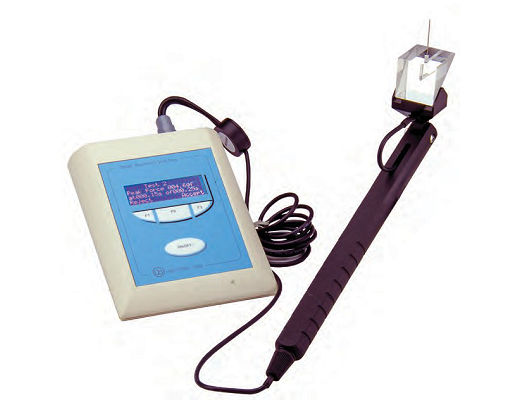
足底触觉仪-尊龙凯时网娱乐官网
自动化评估大小鼠足底触觉敏感性,用于镇痛药物研究、伤害性疼痛、 神经病理学、术后疼痛等研究过程中的异常性疼痛和痛觉过敏测试。
von frey 纤维丝是临床及临床前科研领域,神经病理学疼痛行为评估的传统方法,但其测试过程繁琐且乏味,实验人员不易掌握计算方法,容易出错。
ugo basile 动态足底测试仪是以电子刺痛仪为基础优化而来的全自动刺痛尊龙凯时网娱乐官网的解决方案,可直接测量大小鼠疼痛疾病模型中的疼痛阈值。除了具有简化von frey纤维丝刺痛方案,拥有电子刺痛仪自动检测、**定位等优势外,还具有刺痛角度固定无偏差,施力可预设等特点,极大的减小了实验者测试结果的随机误差,提高了测试结果可重复性。
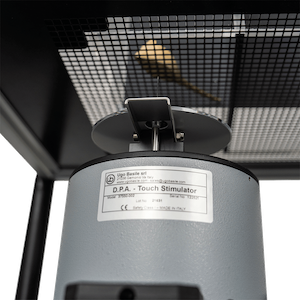
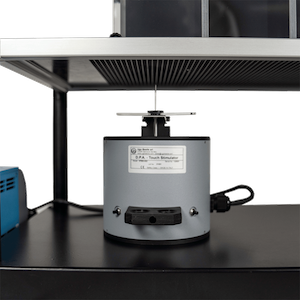
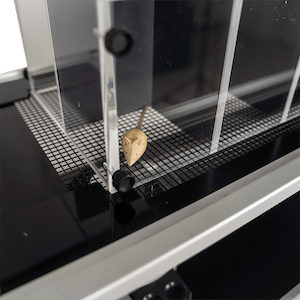
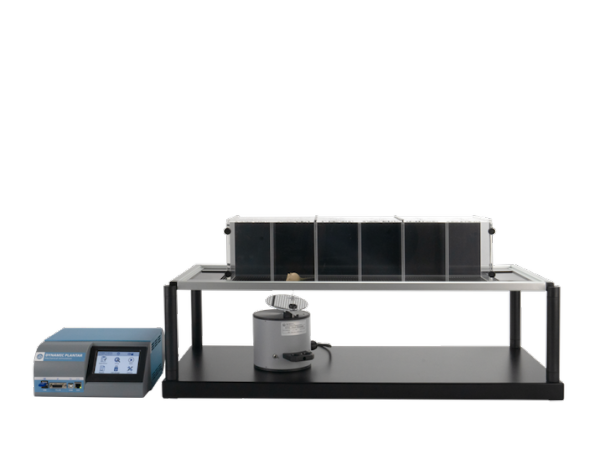
设备由带有金属针的基座、测试台、控制主机等构成。大小鼠放置在测试平台隔间内,将基座上垂直固定的金属针对准动物足底,金属针将以预设的力量大小和变化速度对大小鼠进行刺痛。当动物出现缩足、舔足、跳跃等情况时,机械刺激自动停止,自动记录疼痛阈值。

优势特点:
1. **控制垂直施力方向无偏差
相较于电子测痛仪手持式刺痛方式,动态足底刺痛仪的金属针固定于基座上,可**控制金属针施力过程中与足底垂直不发生任何方向上的偏差。
2. 可预设施力斜率
手持式电子刺痛仪,施加压力因为个体操作差异的方式存在偏差,无法达到完美的施力稳定性。动态足底刺痛仪可预设恒定的施压斜率,简化了操作流程,提高了数据准确度。
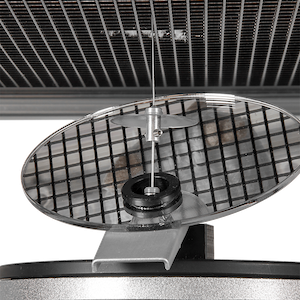
3. 独特的折射镜设计,定位**
精确定位刺痛位置在测试过程中往往不易掌握,这给研究者们带来一定困扰。动态足底刺痛仪使用的内嵌式传感器带有圆形凹面折射镜,可快速定位足底刺痛位点。
4. 自动检测动物缩足反应,无需人为判断
当痛阈出现动物出现缩足、舔足、跳跃等情况时,仪器自动记录出现压力峰值时间和大小。
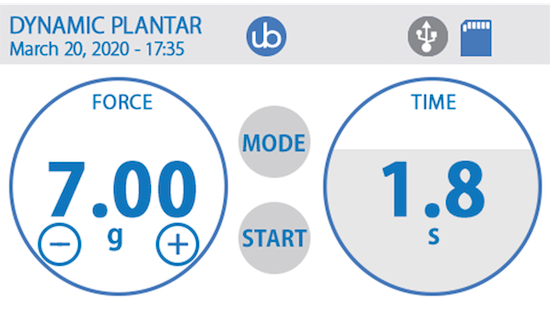
5.0.1-100g测量范围,0.1g高精度分辨率
动态足底刺痛仪施力范围和分辨率可满足众多疼痛研究,同时也保证了的测试的灵敏度。

应用领域:
动态足底测试仪用于神经损伤等各种应用中,如坐骨神经结扎(pnl)、慢性收缩损伤(cci)和脊神经结扎(snl)疾病模型,帮助大量使用者进行疼痛分子研究和筛选**异常性疼痛和痛觉过敏的药物。

型号规格:
37550 | 动态足底测试仪完整套装,包括控制主机、测试基座、测试台等 |
37102 | 中号大鼠固定器(选配) |
37103 | 大号大鼠固定器(选配) |
参考文献:
1.friščić, jasna, et al. "the complement system drives local inflammatory tissue priming by metabolic reprogramming of synovial fibroblasts." immunity 54.5 (2021): 1002-1021. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.03.003
2.boyd, jacob t., et al. "elevated dietary ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids induce reversible peripheral nerve dysfunction that exacerbates comorbid pain conditions." nature metabolism 3.6 (2021): 762-773.doi:
3.defaye, manon, et al. "the neuronal tyrosine kinase receptor ligand alkal2 mediates persistent pain." the journal of clinical investigation 132.12 (2022).doi: 10.1172/jci154317
4.liu, shijia, et al. "divergent brainstem opioidergic pathways that coordinate breathing with pain and emotions." neuron 110.5 (2022): 857-873. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2021.11.029
5.powell, rasheen, et al. "inhibiting endocytosis in cgrp nociceptors attenuates inflammatory pain-like behavior." nature communications 12.1 (2021): 5812. 10.1038/s41467-021-26100-6
6.cheong, hogyun, et al. "sutureless neurorrhaphy system using a macrophage-polarizing in situ visible light-crosslinkable adhesive protein hydrogel for functional nerve regeneration." chemical engineering journal 445 (2022): 136641.
doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.136641
7.llorca-torralba, meritxell, et al. "pain and depression comorbidity causes asymmetric plasticity in the locus coeruleus neurons." brain 145.1 (2022): 154-167. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab239
8.sohn, hee su, et al. "tolerogenic nanoparticles induce type ii collagen–specific regulatory t cells and ameliorate osteoarthritis." science advances 8.47 (2022): eabo5284.doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo5284
9.fotio, yannick, et al. "naaa-regulated lipid signaling governs the transition from acute to chronic pain." science advances 7.43 (2021): eabi8834.doi:10.1126/sciadv.abi8834
10.kolbinger, anja, et al. "eosinophil‐derived il‐4 is necessary to establish the inflammatory structure in innate inflammation." embo molecular medicine 15.2 (2023): e16796.
自动化评估大小鼠足底触觉敏感性,用于镇痛药物研究、伤害性疼痛、 神经病理学、术后疼痛等研究过程中的异常性疼痛和痛觉过敏测试。
von frey 纤维丝是临床及临床前科研领域,神经病理学疼痛行为评估的传统方法,但其测试过程繁琐且乏味,实验人员不易掌握计算方法,容易出错。
ugo basile 动态足底测试仪是以电子刺痛仪为基础优化而来的全自动刺痛尊龙凯时网娱乐官网的解决方案,可直接测量大小鼠疼痛疾病模型中的疼痛阈值。除了具有简化von frey纤维丝刺痛方案,拥有电子刺痛仪自动检测、**定位等优势外,还具有刺痛角度固定无偏差,施力可预设等特点,极大的减小了实验者测试结果的随机误差,提高了测试结果可重复性。
设备由带有金属针的基座、测试台、控制主机等构成。大小鼠放置在测试平台隔间内,将基座上垂直固定的金属针对准动物足底,金属针将以预设的力量大小和变化速度对大小鼠进行刺痛。当动物出现缩足、舔足、跳跃等情况时,机械刺激自动停止,自动记录疼痛阈值。

优势特点:
1. **控制垂直施力方向无偏差
相较于电子测痛仪手持式刺痛方式,动态足底刺痛仪的金属针固定于基座上,可**控制金属针施力过程中与足底垂直不发生任何方向上的偏差。
2. 可预设施力斜率
手持式电子刺痛仪,施加压力因为个体操作差异的方式存在偏差,无法达到完美的施力稳定性。动态足底刺痛仪可预设恒定的施压斜率,简化了操作流程,提高了数据准确度。
3. 独特的折射镜设计,定位**
精确定位刺痛位置在测试过程中往往不易掌握,这给研究者们带来一定困扰。动态足底刺痛仪使用的内嵌式传感器带有圆形凹面折射镜,可快速定位足底刺痛位点。
4. 自动检测动物缩足反应,无需人为判断
当痛阈出现动物出现缩足、舔足、跳跃等情况时,仪器自动记录出现压力峰值时间和大小。
5.0.1-100g测量范围,0.1g高精度分辨率
动态足底刺痛仪施力范围和分辨率可满足众多疼痛研究,同时也保证了的测试的灵敏度。


应用领域:
动态足底测试仪用于神经损伤等各种应用中,如坐骨神经结扎(pnl)、慢性收缩损伤(cci)和脊神经结扎(snl)疾病模型,帮助大量使用者进行疼痛分子研究和筛选**异常性疼痛和痛觉过敏的药物。




型号规格:
37550 | 动态足底测试仪完整套装,包括控制主机、测试基座、测试台等 |
37102 | 中号大鼠固定器(选配) |
37103 | 大号大鼠固定器(选配) |

参考文献:
1.friščić, jasna, et al. "the complement system drives local inflammatory tissue priming by metabolic reprogramming of synovial fibroblasts." immunity 54.5 (2021): 1002-1021. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.03.003
2.boyd, jacob t., et al. "elevated dietary ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids induce reversible peripheral nerve dysfunction that exacerbates comorbid pain conditions." nature metabolism 3.6 (2021): 762-773.doi:
3.defaye, manon, et al. "the neuronal tyrosine kinase receptor ligand alkal2 mediates persistent pain." the journal of clinical investigation 132.12 (2022).doi: 10.1172/jci154317
4.liu, shijia, et al. "divergent brainstem opioidergic pathways that coordinate breathing with pain and emotions." neuron 110.5 (2022): 857-873. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2021.11.029
5.powell, rasheen, et al. "inhibiting endocytosis in cgrp nociceptors attenuates inflammatory pain-like behavior." nature communications 12.1 (2021): 5812. 10.1038/s41467-021-26100-6
6.cheong, hogyun, et al. "sutureless neurorrhaphy system using a macrophage-polarizing in situ visible light-crosslinkable adhesive protein hydrogel for functional nerve regeneration." chemical engineering journal 445 (2022): 136641.
doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.136641
7.llorca-torralba, meritxell, et al. "pain and depression comorbidity causes asymmetric plasticity in the locus coeruleus neurons." brain 145.1 (2022): 154-167. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab239
8.sohn, hee su, et al. "tolerogenic nanoparticles induce type ii collagen–specific regulatory t cells and ameliorate osteoarthritis." science advances 8.47 (2022): eabo5284.doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo5284
9.fotio, yannick, et al. "naaa-regulated lipid signaling governs the transition from acute to chronic pain." science advances 7.43 (2021): eabi8834.doi:10.1126/sciadv.abi8834
10.kolbinger, anja, et al. "eosinophil‐derived il‐4 is necessary to establish the inflammatory structure in innate inflammation." embo molecular medicine 15.2 (2023): e16796.
 浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~
浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~