取消
清空记录
历史记录
清空记录
历史记录


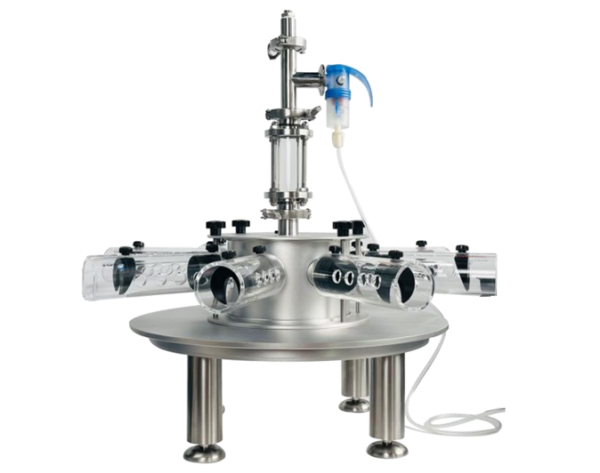
1030型小动物核磁兼容监护&门控系统 -尊龙凯时网娱乐官网
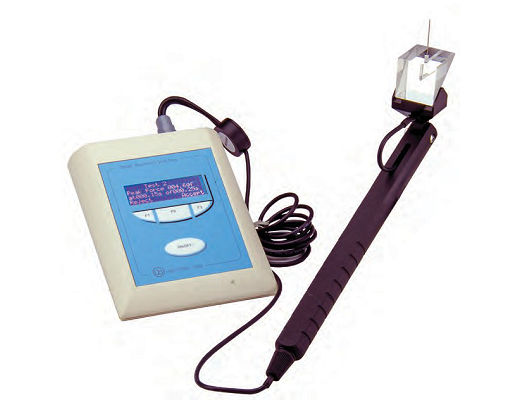
用于实验室、pet、ct、spect、光学、核磁环境中处于麻醉状态下的大小鼠以及其他稍大动物的生理监测和门控成像。
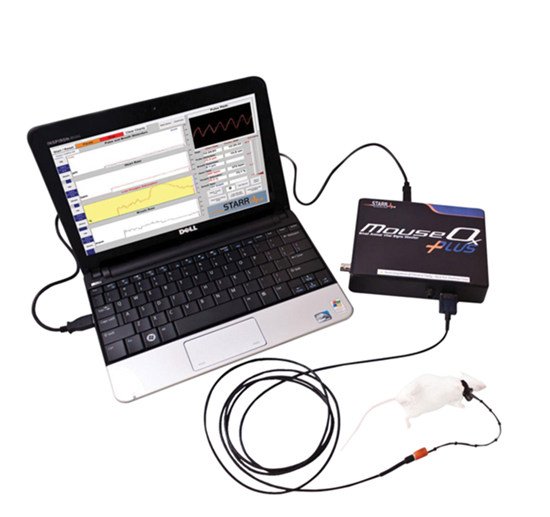
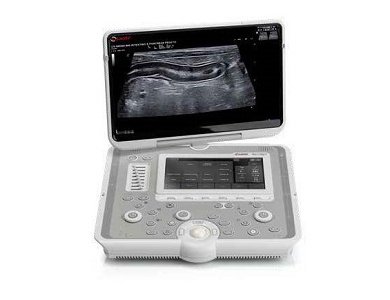
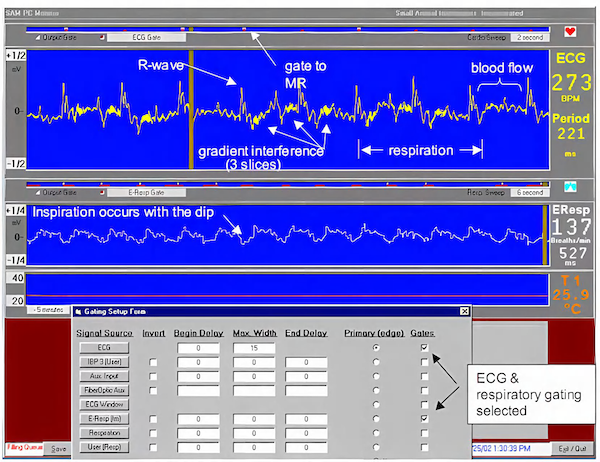
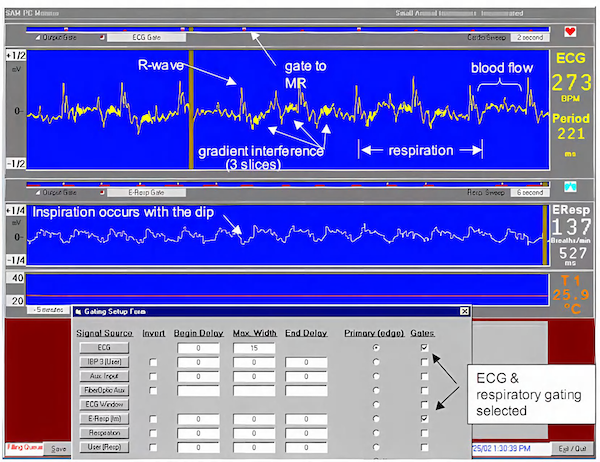
小动物监护&门控系统系统用于麻醉大小鼠及较大动物生理状态监护,可以搭配核磁兼容装置,核磁环境下监护大小鼠心电、呼吸和体温,模块化设计使用更加简单方便。该系统包括一个ert模块和一个ert控制器,pc可显示多个波形、测量值和趋势。门控通过监测动物的心电呼吸信号,将图像采集与心脏和呼吸的特定时相相匹配,舍弃一些主动运动期间的信号采集,通过对运动的监测来达到抑制运动伪影的效果,增强图像质量。
优势特点:
1. 可在ct、pet、spect、光学成像、正常实验环境工作
2. pc实时显示监测生理参数波形及数值、门控点设置等信息
3. 模块化设计,用户根据需求选配,节约实验成本
4. 可监测呼吸心电体温等参数
5. r波门控延迟可由用户设置,呼吸门控宽度可由用户设置
6. 可选配脉搏血氧、etco2、有创血压、光纤测温及通气辅助等功能
7. 可搭配核磁兼容模块,兼容mr环境,可在高磁场环境下工作
应用领域:
小动物核磁兼容监护&门控系统广泛应用于各种mr、mri、ct、pet ct成像中,将图像采集与心脏和呼吸的特定时相相匹配,舍弃一些主动运动期间的信号采集,通过对运动的监测来达到抑制运动伪影的效果,增强图像质量。


图为小鼠主动脉根部:9.4t垂直场;心电图和呼吸门控;90秒图像,无对比度
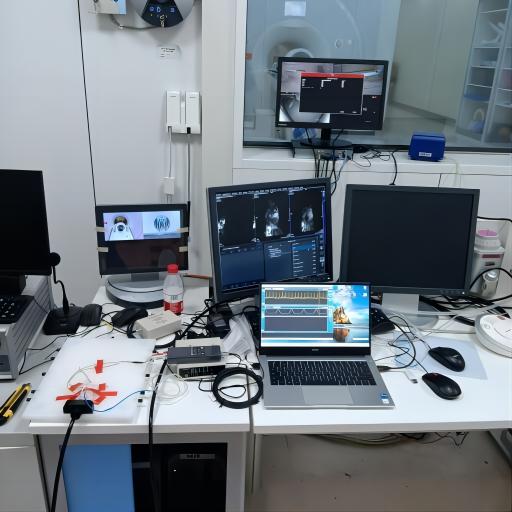
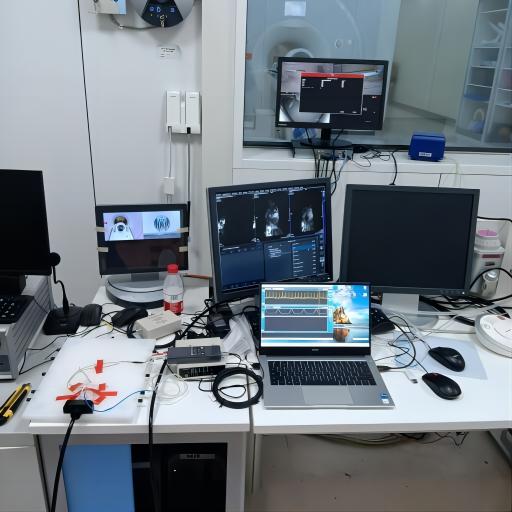


图为西门子7.0tterra科研临床两用磁共振, 安装sall动物门控扫描减少伪影和心电监护
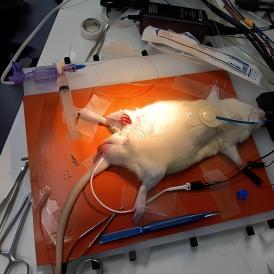
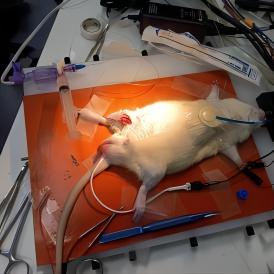
图为门控有创血压模块监测股动脉

图为1030型在核磁环境下应用于灵长类动物颅脑部的监护门控
部分用户名单:
| 上海市东方医院 | 上海交通大学医学院 | 中科院自动化研究所 |
| 复旦**医院 | 上海科技大学 | 中科院神经所 |
| 协和医院 | 北京大学 | 中科院生物物理所 |
| 北京大学第三附属医院 | 清华大学 | 昆明动物研究所 |
| 湘雅一附院 | 首都医科大学 | 上海联影医疗科技股份有限公司 |
型号规格:
| 1025t | 门控模块、心电呼吸和体温监测模块、选配模块及其他电源和连接线 | |
| 1030 | 核磁兼容模块、门控模块、心电呼吸和体温监测模块、选配模块及其他电源和连接线 | |
参考文献:
1.zhao, qiulong et al. “phytomedicine fructus aurantii-derived two absorbed compounds unlock antidepressant and prokinetic multi-functions via modulating 5-ht3/ghsr.” journal of ethnopharmacology vol. 323 (2024): 117703. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117703
2.alvarado, roman et al. “real-time imaging of decompression gas bubble growth in the spinal cord of live rats.” magnetic resonance in medicine, 10.1002/mrm.30128. 23 apr. 2024, doi:10.1002/mrm.30128
3.duan, chenwei et al. “in vivo visualization and quantification of rat laryngeal blood supply after hydration challenge.” the laryngoscope vol. 134,2 (2024): 779-785. doi:10.1002/lary.30965
4.warias, jonas erik et al. “the laser pump x-ray probe system at lisa p08 petra iii.” journal of synchrotron radiation, 10.1107/s1600577524003400. 1 jul. 2024, doi:10.1107/s1600577524003400
5.schweins, moritz et al. “multi-modal assessment of a cardiac stem cell therapy reveals distinct modulation of regional scar properties.” journal of translational medicine vol. 22,1 187. 21 feb. 2024, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-04986-2
6.chan, dennis c et al. “cytokine expression patterns predict suppression of vulnerable neural circuits in a mouse model of alzheimer's disease.” biorxiv : the preprint server for biology 2024.03.17.585383. 17 mar. 2024, doi:10.1101/2024.03.17.585383. preprint.
7.yen, tin-yo c et al. “biocompatible and bioactivable terpolymer-lipid-mno2 nanoparticle-based mri contrast agent for improving tumor detection and delineation.” materials today. bio vol. 25 100954. 17 jan. 2024, doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100954
8.suarez, aileen c et al. “pregnancy-induced remodeling of the murine reproductive tract: a longitudinal in vivo magnetic resonance imaging study.” scientific reports vol. 14,1 586. 5 jan. 2024, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-50437-1
9.robinson, gain et al. “multimodal imaging reveals that sustained inhibition of hif-prolyl hydroxylases induces opposing effects on right and left ventricular function in healthy rats.” molecular imaging and biology vol. 26,1 (2024): 179-187. doi:10.1007/s11307-023-01876-9
10.zhao, qiulong et al. “phytomedicine fructus aurantii-derived two absorbed compounds unlock antidepressant and prokinetic multi-functions via modulating 5-ht3/ghsr.” journal of ethnopharmacology vol. 323 (2024): 117703. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117703
11.hune, theresa et al. “metabolic tumor imaging with rapidly signal-enhanced 1-13 c-pyruvate-d3.” chemphyschem : a european journal of chemical physics and physical chemistry vol. 24,2 (2023): e202200615. doi:10.1002/cphc.202200615
12.wunker, claire et al. “magnetic resonance-guided high intensity focused ultrasound generated hyperthermia: a feasible treatment method in a murine rhabdomyosarcoma model.” journal of visualized experiments : jove ,191 10.3791/64544. 13 jan. 2023, doi:10.3791/64544
13.burns, jennie m et al. “dilation of the superior sagittal sinus detected in rat model of mild traumatic brain injury using 1 t magnetic resonance imaging.” frontiers in neurology vol. 14 1045695. 26 apr. 2023, doi:10.3389/fneur.2023.1045695
14.jendritza, patrick et al. “multi-area recordings and optogenetics in the awake, behaving marmoset.” nature communications vol. 14,1 577. 2 feb. 2023, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36217-5
cabral, joana et al. “intrinsic macroscale oscillatory modes driving long range functional connectivity in female rat brains detected by ultrafast fmri.” nature communications vol. 14,1 375. 6 feb. 2023, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36025-x
您想了解更多详细资料吗?
请与我们联系:
tel:021-35183767,021-54377179
18502129044
qq:3007536033
微信:yuyanbio
mail:yuyanbio@126.com
欢迎您的咨询!

用于实验室、pet、ct、spect、光学、核磁环境中处于麻醉状态下的大小鼠以及其他稍大动物的生理监测和门控成像。
小动物监护&门控系统系统用于麻醉大小鼠及较大动物生理状态监护,可以搭配核磁兼容装置,核磁环境下监护大小鼠心电、呼吸和体温,模块化设计使用更加简单方便。该系统包括一个ert模块和一个ert控制器,pc可显示多个波形、测量值和趋势。门控通过监测动物的心电呼吸信号,将图像采集与心脏和呼吸的特定时相相匹配,舍弃一些主动运动期间的信号采集,通过对运动的监测来达到抑制运动伪影的效果,增强图像质量。


优势特点:
1. 可在ct、pet、spect、光学成像、正常实验环境工作
2. pc实时显示监测生理参数波形及数值、门控点设置等信息
3. 模块化设计,用户根据需求选配,节约实验成本
4. 可监测呼吸心电体温等参数
5. r波门控延迟可由用户设置,呼吸门控宽度可由用户设置
6. 可选配脉搏血氧、etco2、有创血压、光纤测温及通气辅助等功能
7. 可搭配核磁兼容模块,兼容mr环境,可在高磁场环境下工作
应用领域:
小动物核磁兼容监护&门控系统广泛应用于各种mr、mri、ct、pet ct成像中,将图像采集与心脏和呼吸的特定时相相匹配,舍弃一些主动运动期间的信号采集,通过对运动的监测来达到抑制运动伪影的效果,增强图像质量。


图为小鼠主动脉根部:9.4t垂直场;心电图和呼吸门控;90秒图像,无对比度


图为西门子7.0tterra科研临床两用磁共振, 安装sall动物门控扫描减少伪影和心电监护


图为门控有创血压模块监测股动脉

图为1030型在核磁环境下应用于灵长类动物颅脑部的监护门控
部分用户名单:
| 上海市东方医院 | 上海交通大学医学院 | 中科院自动化研究所 |
| 复旦**医院 | 上海科技大学 | 中科院神经所 |
| 协和医院 | 北京大学 | 中科院生物物理所 |
| 北京大学第三附属医院 | 清华大学 | 昆明动物研究所 |
| 湘雅一附院 | 首都医科大学 | 上海联影医疗科技股份有限公司 |
型号规格:
| 1025t | 门控模块、心电呼吸和体温监测模块、选配模块及其他电源和连接线 | |
| 1030 | 核磁兼容模块、门控模块、心电呼吸和体温监测模块、选配模块及其他电源和连接线 | |
参考文献:
1.zhao, qiulong et al. “phytomedicine fructus aurantii-derived two absorbed compounds unlock antidepressant and prokinetic multi-functions via modulating 5-ht3/ghsr.” journal of ethnopharmacology vol. 323 (2024): 117703. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117703
2.alvarado, roman et al. “real-time imaging of decompression gas bubble growth in the spinal cord of live rats.” magnetic resonance in medicine, 10.1002/mrm.30128. 23 apr. 2024, doi:10.1002/mrm.30128
3.duan, chenwei et al. “in vivo visualization and quantification of rat laryngeal blood supply after hydration challenge.” the laryngoscope vol. 134,2 (2024): 779-785. doi:10.1002/lary.30965
4.warias, jonas erik et al. “the laser pump x-ray probe system at lisa p08 petra iii.” journal of synchrotron radiation, 10.1107/s1600577524003400. 1 jul. 2024, doi:10.1107/s1600577524003400
5.schweins, moritz et al. “multi-modal assessment of a cardiac stem cell therapy reveals distinct modulation of regional scar properties.” journal of translational medicine vol. 22,1 187. 21 feb. 2024, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-04986-2
6.chan, dennis c et al. “cytokine expression patterns predict suppression of vulnerable neural circuits in a mouse model of alzheimer's disease.” biorxiv : the preprint server for biology 2024.03.17.585383. 17 mar. 2024, doi:10.1101/2024.03.17.585383. preprint.
7.yen, tin-yo c et al. “biocompatible and bioactivable terpolymer-lipid-mno2 nanoparticle-based mri contrast agent for improving tumor detection and delineation.” materials today. bio vol. 25 100954. 17 jan. 2024, doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100954
8.suarez, aileen c et al. “pregnancy-induced remodeling of the murine reproductive tract: a longitudinal in vivo magnetic resonance imaging study.” scientific reports vol. 14,1 586. 5 jan. 2024, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-50437-1
9.robinson, gain et al. “multimodal imaging reveals that sustained inhibition of hif-prolyl hydroxylases induces opposing effects on right and left ventricular function in healthy rats.” molecular imaging and biology vol. 26,1 (2024): 179-187. doi:10.1007/s11307-023-01876-9
10.zhao, qiulong et al. “phytomedicine fructus aurantii-derived two absorbed compounds unlock antidepressant and prokinetic multi-functions via modulating 5-ht3/ghsr.” journal of ethnopharmacology vol. 323 (2024): 117703. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117703
11.hune, theresa et al. “metabolic tumor imaging with rapidly signal-enhanced 1-13 c-pyruvate-d3.” chemphyschem : a european journal of chemical physics and physical chemistry vol. 24,2 (2023): e202200615. doi:10.1002/cphc.202200615
12.wunker, claire et al. “magnetic resonance-guided high intensity focused ultrasound generated hyperthermia: a feasible treatment method in a murine rhabdomyosarcoma model.” journal of visualized experiments : jove ,191 10.3791/64544. 13 jan. 2023, doi:10.3791/64544
13.burns, jennie m et al. “dilation of the superior sagittal sinus detected in rat model of mild traumatic brain injury using 1 t magnetic resonance imaging.” frontiers in neurology vol. 14 1045695. 26 apr. 2023, doi:10.3389/fneur.2023.1045695
14.jendritza, patrick et al. “multi-area recordings and optogenetics in the awake, behaving marmoset.” nature communications vol. 14,1 577. 2 feb. 2023, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36217-5
cabral, joana et al. “intrinsic macroscale oscillatory modes driving long range functional connectivity in female rat brains detected by ultrafast fmri.” nature communications vol. 14,1 375. 6 feb. 2023, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36025-x
您想了解更多详细资料吗?
请与我们联系:
tel:021-35183767,021-54377179
18502129044
qq:3007536033
微信:yuyanbio
mail:yuyanbio@126.com
欢迎您的咨询!
 浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~
浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~