取消
清空记录
历史记录
清空记录
历史记录


ugo basile双足平衡测试仪-尊龙凯时网娱乐官网
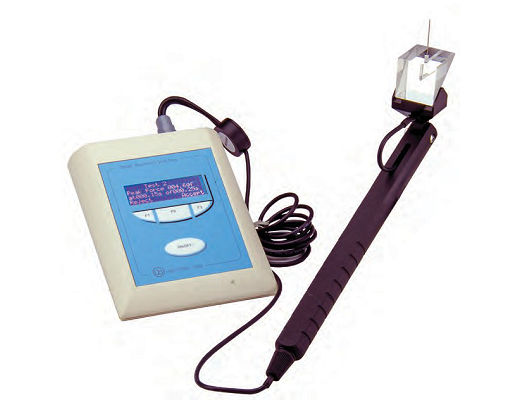
测量小鼠或大鼠后爪之间的重量分布差异,用于评估骨关节炎、骨*、神经损伤和术后疼痛研究中的自发性疼痛。自动测量减少操作偏差、优化重复性以及节约时间。
诱发性疼痛敏感测试通常由多类机械、冷热刺激完成,而对于如何较好地客观测量自发性疼痛行为,经典的实验方案是双足平衡测试,且具有不可替代性。
ugo basile双足平衡测试仪通过测量动物在无约束的情况下炎症疼痛足与正常足的重量分布差异,是目前筛选镇痛**药物药效较好的一种方法。双足平衡测试法克服了诱发机械痛测试可能引起的动物紧张或操作人员主观性问题,该设备采用双通道重量平均法,可以同时对一只动物进行自动测量,具有减少操作偏差、优化重复性以及节省时间等优点。
通常将动物置于具有倾斜面的有机玻璃适配器中,迫使动物后爪置于两个**的压力传感器上,通过静态承重或失能分析,测量整个后肢的重量分布。动物两侧脚掌重量分布不均的现象,被认为是对痛觉感受程度的自然调节,差别越大说明炎症足越疼痛,使用有镇痛作用的药可以减少其差别,以此方法可来鉴定**、镇痛药物的药效。
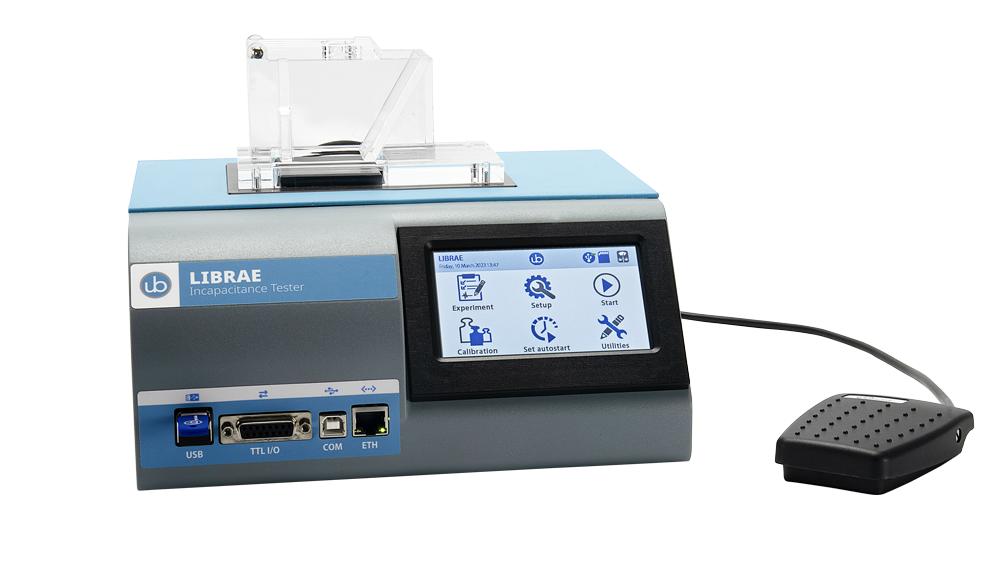

优势特征:
一、关节炎研究的经典工具
关节是全身应力传导中重要环节,具有支撑躯体作用。关节的炎性或非炎性疼痛多具有慢性和隐匿性的特点,对其测量自发疼痛行为具有难度。大量研究表明,双足平衡在各类关节炎疼痛模型中敏感性更高
二、测量过程自动化,实验结果可视化程度高
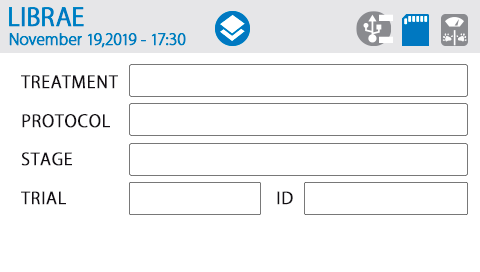
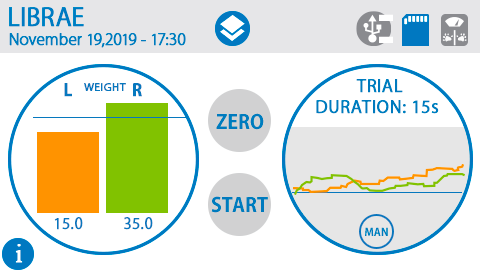
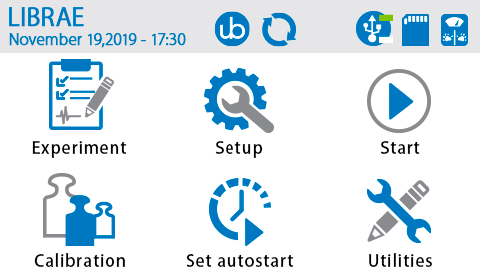
具有autostart功能,可实现以一致的条件进行每次实验,减少测量过程中的可变性和实验人员的偏差或干预。相较于其他同类产品,简明的触摸屏界面,无复杂操作环节,研究人员可快速上手。测试过程中直接显示双侧重力变化曲线图,可视化程度高。
三、高分辨率传感器精确捕捉重力差异
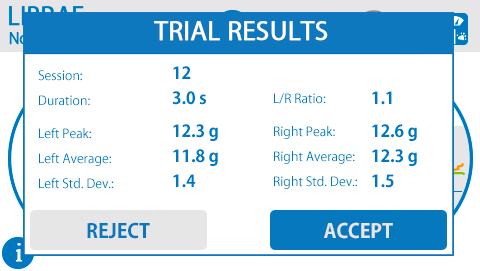
采用0.1克高分辨率传感器可检测大小鼠双边重量差异,配备参考砝码可快速进行传感器校准。并且测试平台上没有其他可能干扰动物的组件,因此可获得较好的实验重复性。
四、动物自发性表征,数据无主观偏倚
数据偏倚是疼痛研究中的一个常见问题,因为实验者是基于主观行为观察和干预的,来自动物应激反应的干扰不可避免。双足平衡测试仪提供了一种偏差*小化的方法,增加了研究者对数据的信心,实验数据更具说服力。
应用领域:
双足平衡测试仪可用于评估骨关节炎、软骨退化、骨*、神经损伤和术后疼痛等大小鼠动物模型的后爪疼痛水平,进行镇痛**相关药物的筛选,尤其在骨关节炎研究中应用广。

型号规格:
47885 | 大小鼠通用型完整套装,包括控制主机、大鼠适配器、小鼠适配器等 |
47882 | 大鼠通用型完整套装,包括控制主机、大鼠适配器等 |
47883 | 小鼠通用型完整套装,包括控制主机、小鼠适配器等 |
47880-002 | 大鼠适配器(选配) |
47880-003 | 小鼠适配器(选配) |
47880-004 | 肥胖大鼠适配器(选配) |
参考文献:
1.argueta, donovan a., et al. "palmitoylethanolamide attenuates pain-like behavior in factor viii deficient mice." blood 140.supplement 1 (2022): 5578-5579.doi:10.1182/blood-2022-159745
2.shi, yuanyuan et al. “a small molecule promotes cartilage extracellular matrix generation and inhibits osteoarthritis development.” nature communications vol. 10,1 1914. 23 apr. 2019, doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09839-x
3.cao, chenxi et al. “cholesterol-induced lrp3 downregulation promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by targeting syndecan-4.” nature communications vol. 13,1 7139. 21 nov. 2022, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-34830-4
4.kwon, hyuk-kwon et al. “a cell-penetrating peptide blocks toll-like receptor-mediated downstream signaling and ameliorates autoimmune and inflammatory diseases in mice.” experimental & molecular medicine vol. 51,4 1-19. 26 apr. 2019, doi:10.1038/s12276-019-0244-0
5.batchelor, v., j. miotla-zarebska, and t. l. vincent. "refining methods to measure spontaneous pain behaviour in surgically induced murine osteoarthritis." osteoarthritis and cartilage 30 (2022): s381. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2022.02.513
6.cheng, jin, et al. "rip1 perturbation induces chondrocyte necroptosis and promotes osteoarthritis pathogenesis via targeting bmp7." frontiers in cell and developmental biology 9 (2021): 638382. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.638382
7.sur, bongjun et al. “inhibition of carrageenan/kaolin-induced arthritis in rats and of inflammatory cytokine expressions in human il-1β-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes by a benzylideneacetophenone derivative.” inflammation vol. 42,3 (2019): 928-936. doi:10.1007/s10753-018-0947-8
8.villa, thea et al. “fangchinoline has an anti-arthritic effect in two animal models and in il-1β-stimulated human fls cells.” biomolecules & therapeutics vol. 28,5 (2020): 414-422. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2020.113
9.carlesso, lisa c et al. “use of immpact recommendations to explore pain phenotypes in people with knee osteoarthritis.” pain medicine (malden, mass.) vol. 23,10 (2022): 1708-1716. doi:10.1093/pm/pnac044
10.surcheva, slavina, et al. "preclinic and clinic effectiveness of gabapentin and pregabalin for treatment of neuropathic pain in rats and diabetic patients." biotechnology & biotechnological equipment 31.3 (2017): 568-573.doi:10.1080/13102818.2017.1290550
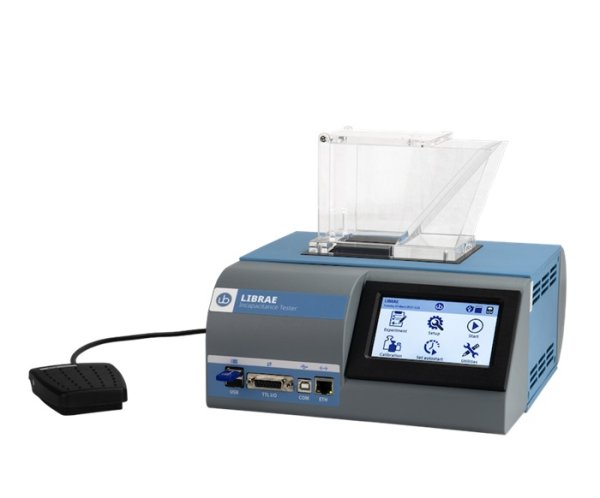
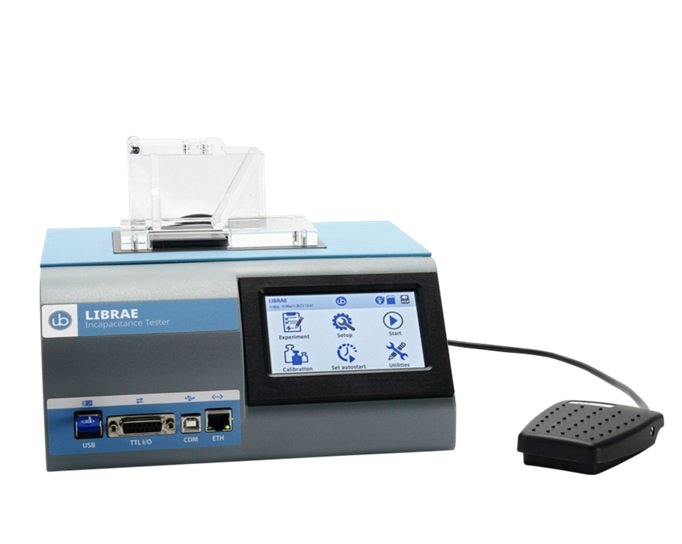






测量小鼠或大鼠后爪之间的重量分布差异,用于评估骨关节炎、骨*、神经损伤和术后疼痛研究中的自发性疼痛。自动测量减少操作偏差、优化重复性以及节约时间。
诱发性疼痛敏感测试通常由多类机械、冷热刺激完成,而对于如何较好地客观测量自发性疼痛行为,经典的实验方案是双足平衡测试,且具有不可替代性。
ugo basile双足平衡测试仪通过测量动物在无约束的情况下炎症疼痛足与正常足的重量分布差异,是目前筛选镇痛**药物药效较好的一种方法。双足平衡测试法克服了诱发机械痛测试可能引起的动物紧张或操作人员主观性问题,该设备采用双通道重量平均法,可以同时对一只动物进行自动测量,具有减少操作偏差、优化重复性以及节省时间等优点。
通常将动物置于具有倾斜面的有机玻璃适配器中,迫使动物后爪置于两个**的压力传感器上,通过静态承重或失能分析,测量整个后肢的重量分布。动物两侧脚掌重量分布不均的现象,被认为是对痛觉感受程度的自然调节,差别越大说明炎症足越疼痛,使用有镇痛作用的药可以减少其差别,以此方法可来鉴定**、镇痛药物的药效。

优势特征:
一、关节炎研究的经典工具
关节是全身应力传导中重要环节,具有支撑躯体作用。关节的炎性或非炎性疼痛多具有慢性和隐匿性的特点,对其测量自发疼痛行为具有难度。大量研究表明,双足平衡在各类关节炎疼痛模型中敏感性更高
二、测量过程自动化,实验结果可视化程度高
具有autostart功能,可实现以一致的条件进行每次实验,减少测量过程中的可变性和实验人员的偏差或干预。相较于其他同类产品,简明的触摸屏界面,无复杂操作环节,研究人员可快速上手。测试过程中直接显示双侧重力变化曲线图,可视化程度高。
三、高分辨率传感器精确捕捉重力差异
采用0.1克高分辨率传感器可检测大小鼠双边重量差异,配备参考砝码可快速进行传感器校准。并且测试平台上没有其他可能干扰动物的组件,因此可获得较好的实验重复性。
四、动物自发性表征,数据无主观偏倚
数据偏倚是疼痛研究中的一个常见问题,因为实验者是基于主观行为观察和干预的,来自动物应激反应的干扰不可避免。双足平衡测试仪提供了一种偏差*小化的方法,增加了研究者对数据的信心,实验数据更具说服力。


应用领域:
双足平衡测试仪可用于评估骨关节炎、软骨退化、骨*、神经损伤和术后疼痛等大小鼠动物模型的后爪疼痛水平,进行镇痛**相关药物的筛选,尤其在骨关节炎研究中应用广。

型号规格:
47885 | 大小鼠通用型完整套装,包括控制主机、大鼠适配器、小鼠适配器等 |
47882 | 大鼠通用型完整套装,包括控制主机、大鼠适配器等 |
47883 | 小鼠通用型完整套装,包括控制主机、小鼠适配器等 |
47880-002 | 大鼠适配器(选配) |
47880-003 | 小鼠适配器(选配) |
47880-004 | 肥胖大鼠适配器(选配) |
参考文献:
1.argueta, donovan a., et al. "palmitoylethanolamide attenuates pain-like behavior in factor viii deficient mice." blood 140.supplement 1 (2022): 5578-5579.doi:10.1182/blood-2022-159745
2.shi, yuanyuan et al. “a small molecule promotes cartilage extracellular matrix generation and inhibits osteoarthritis development.” nature communications vol. 10,1 1914. 23 apr. 2019, doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09839-x
3.cao, chenxi et al. “cholesterol-induced lrp3 downregulation promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by targeting syndecan-4.” nature communications vol. 13,1 7139. 21 nov. 2022, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-34830-4
4.kwon, hyuk-kwon et al. “a cell-penetrating peptide blocks toll-like receptor-mediated downstream signaling and ameliorates autoimmune and inflammatory diseases in mice.” experimental & molecular medicine vol. 51,4 1-19. 26 apr. 2019, doi:10.1038/s12276-019-0244-0
5.batchelor, v., j. miotla-zarebska, and t. l. vincent. "refining methods to measure spontaneous pain behaviour in surgically induced murine osteoarthritis." osteoarthritis and cartilage 30 (2022): s381. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2022.02.513
6.cheng, jin, et al. "rip1 perturbation induces chondrocyte necroptosis and promotes osteoarthritis pathogenesis via targeting bmp7." frontiers in cell and developmental biology 9 (2021): 638382. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.638382
7.sur, bongjun et al. “inhibition of carrageenan/kaolin-induced arthritis in rats and of inflammatory cytokine expressions in human il-1β-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes by a benzylideneacetophenone derivative.” inflammation vol. 42,3 (2019): 928-936. doi:10.1007/s10753-018-0947-8
8.villa, thea et al. “fangchinoline has an anti-arthritic effect in two animal models and in il-1β-stimulated human fls cells.” biomolecules & therapeutics vol. 28,5 (2020): 414-422. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2020.113
9.carlesso, lisa c et al. “use of immpact recommendations to explore pain phenotypes in people with knee osteoarthritis.” pain medicine (malden, mass.) vol. 23,10 (2022): 1708-1716. doi:10.1093/pm/pnac044
10.surcheva, slavina, et al. "preclinic and clinic effectiveness of gabapentin and pregabalin for treatment of neuropathic pain in rats and diabetic patients." biotechnology & biotechnological equipment 31.3 (2017): 568-573.doi:10.1080/13102818.2017.1290550
 浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~
浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~