取消
清空记录
历史记录
清空记录
历史记录


微透析采样系统-尊龙凯时网娱乐官网
微透析采样系统(microdialysis)是一种从生物体内进行动态微量生化取样的技术,具有连续取样、动态观察、定量分析、采样量小、组织损伤轻等特点。
主要由微量注射泵,清醒活动装置,微透析探针,自动收集器组成。
本系统在神经科学、医药研究等领域已获得越来越广泛的应用。

微透析采样系统主要原理是将一种具有半透膜的探针置于实验动物的特定组织中, 利用泵推送溶液至探针处,从而使组织内的目标物质通过半透膜扩散到探针内,以达到从组织内取出需要测量的低分子量物质,以便于进一步的分析。这套设备可对麻醉或清醒的动物进行连续的灌流实验,为医学、药学、生命科学等领域的发展提供了崭新的技术。
应用范畴:精神药物学、神经病理研究、药物动态学及毒物学、生理学药理学、生命胺分析、乙酰胆素/胆碱分析、自由基/氨基酸分析、各种组织生化/药物分析。
工作原理:
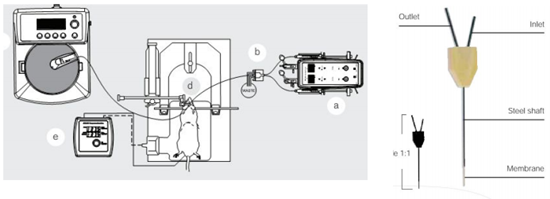
完整的脑部微透析系统包含以下几个部分:
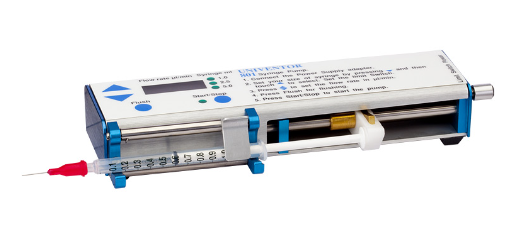
微透析泵
用于连续提供灌流液,微透析泵较高的稳定性和精确性有利于透析实验的进行。
双通道控制泵:

单通道控制泵:
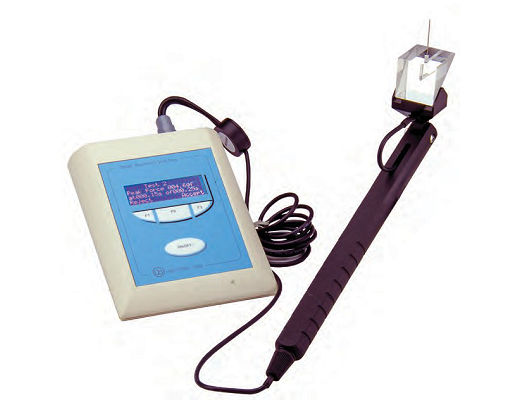
微透析探针
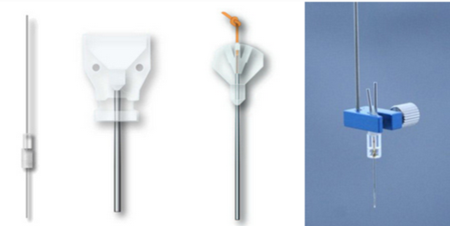
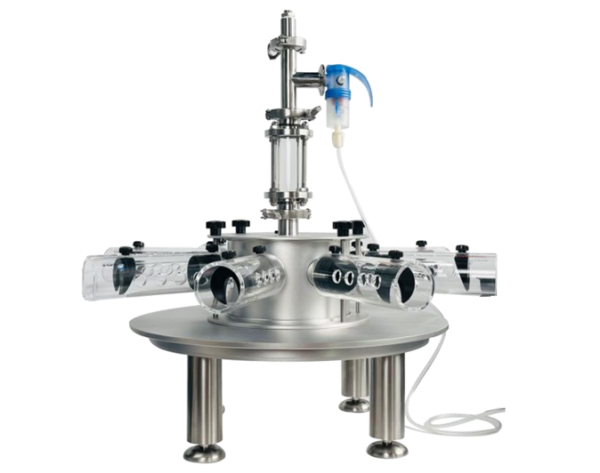
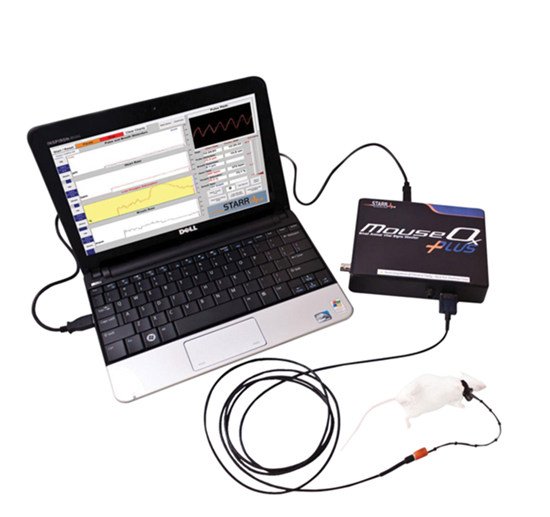
清醒动物活动装置

透析探针附件:
液体切换器,探针支架,管路,接头等,起到导引,定位,固定等作用

微透析液收集器
配合微透析采集系统进行微透析样本的采集和低温保存。
微透析样品收集器,用于样品的低温保存。该仪器具有 20 个样品位,单探针模式下连续收集 20 个样品,或者双探针模式下连续收集 2×10 个样品。可采集 1ul 的样品。保存温度为 8℃
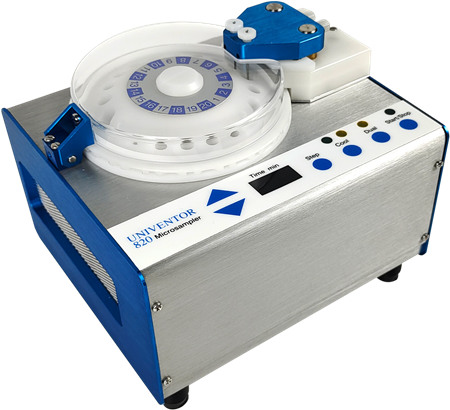

冷却微量收集器可同步收集1–2个透析液,配合双通道微透析泵可同步做2通道微透析取样实验;
冷却温度:8℃;
收集样品数:64 个(300μl瓶)或40个(2ml瓶)
宽屏幕液晶显示4x20字符,rs232及usb接;
参考文献:
fujáková-lipski m, kaping d, šírová j, et al. trans-generational neurochemical modulation of methamphetamine in the adult brain of the wistar rat[j]. archives of toxicology, 2017, 91: 3373-3384.
groessl f, munsch t, meis s, et al. dorsal tegmental dopamine neurons gate associative learning of fear[j]. nature neuroscience, 2018, 21(7): 952-962.
ohara k, fukuda t, ishida y, et al. β-eudesmol, an oxygenized sesquiterpene, stimulates appetite via trpa1 and the autonomic nervous system[j]. scientific reports, 2017, 7(1): 1-16.
klawonn a m, nilsson a, rådberg c f, et al. the sigma-2 receptor selective agonist siramesine (lu 28-179) decreases cocaine-reinforced pavlovian learning and alters glutamatergic and dopaminergic input to the striatum[j]. frontiers in pharmacology, 2017, 8: 714.
suwandi a, bargen i, pils m c, et al. cd4 t cell dependent colitis exacerbation following re-exposure of mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis[j]. frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 2017, 7: 75.
loftén a, adermark l, ericson m, et al. an acetylcholine‐dopamine interaction in the nucleus accumbens and its involvement in ethanol's dopamine‐releasing effect[j]. addiction biology, 2021, 26(3): e12959.
vallöf d, ulenius l, egecioglu e, et al. central administration of the anorexigenic peptide neuromedin u decreases alcohol intake and attenuates alcohol‐induced reward in rodents[j]. addiction biology, 2017, 22(3): 640-651.

微透析采样系统(microdialysis)是一种从生物体内进行动态微量生化取样的技术,具有连续取样、动态观察、定量分析、采样量小、组织损伤轻等特点。
主要由微量注射泵,清醒活动装置,微透析探针,自动收集器组成。
本系统在神经科学、医药研究等领域已获得越来越广泛的应用。

微透析采样系统主要原理是将一种具有半透膜的探针置于实验动物的特定组织中, 利用泵推送溶液至探针处,从而使组织内的目标物质通过半透膜扩散到探针内,以达到从组织内取出需要测量的低分子量物质,以便于进一步的分析。这套设备可对麻醉或清醒的动物进行连续的灌流实验,为医学、药学、生命科学等领域的发展提供了崭新的技术。
应用范畴:精神药物学、神经病理研究、药物动态学及毒物学、生理学药理学、生命胺分析、乙酰胆素/胆碱分析、自由基/氨基酸分析、各种组织生化/药物分析。
工作原理:

完整的脑部微透析系统包含以下几个部分:
微透析泵
用于连续提供灌流液,微透析泵较高的稳定性和精确性有利于透析实验的进行。
双通道控制泵:

单通道控制泵:

微透析探针

清醒动物活动装置

透析探针附件:
液体切换器,探针支架,管路,接头等,起到导引,定位,固定等作用

微透析液收集器
配合微透析采集系统进行微透析样本的采集和低温保存。
微透析样品收集器,用于样品的低温保存。该仪器具有 20 个样品位,单探针模式下连续收集 20 个样品,或者双探针模式下连续收集 2×10 个样品。可采集 1ul 的样品。保存温度为 8℃

冷却微量收集器可同步收集1–2个透析液,配合双通道微透析泵可同步做2通道微透析取样实验;
冷却温度:8℃;
收集样品数:64 个(300μl瓶)或40个(2ml瓶)
宽屏幕液晶显示4x20字符,rs232及usb接;
参考文献:
fujáková-lipski m, kaping d, šírová j, et al. trans-generational neurochemical modulation of methamphetamine in the adult brain of the wistar rat[j]. archives of toxicology, 2017, 91: 3373-3384.
groessl f, munsch t, meis s, et al. dorsal tegmental dopamine neurons gate associative learning of fear[j]. nature neuroscience, 2018, 21(7): 952-962.
ohara k, fukuda t, ishida y, et al. β-eudesmol, an oxygenized sesquiterpene, stimulates appetite via trpa1 and the autonomic nervous system[j]. scientific reports, 2017, 7(1): 1-16.
klawonn a m, nilsson a, rådberg c f, et al. the sigma-2 receptor selective agonist siramesine (lu 28-179) decreases cocaine-reinforced pavlovian learning and alters glutamatergic and dopaminergic input to the striatum[j]. frontiers in pharmacology, 2017, 8: 714.
suwandi a, bargen i, pils m c, et al. cd4 t cell dependent colitis exacerbation following re-exposure of mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis[j]. frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 2017, 7: 75.
loftén a, adermark l, ericson m, et al. an acetylcholine‐dopamine interaction in the nucleus accumbens and its involvement in ethanol's dopamine‐releasing effect[j]. addiction biology, 2021, 26(3): e12959.
vallöf d, ulenius l, egecioglu e, et al. central administration of the anorexigenic peptide neuromedin u decreases alcohol intake and attenuates alcohol‐induced reward in rodents[j]. addiction biology, 2017, 22(3): 640-651.
 浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~
浏览器自带分享功能也很好用哦~