技术交流navigation

电话:021-35183767
021-35183767
传真:021-35183767-8008
qq:2881513768
地址:上海市闵行区兴梅路485号 xingmei rd 485shanghaichina
emms用力肺功能检测系统——临床前动物肺功能检测的经典之作,呼吸系统研究的强大助手
时间:2023-12-15来源:本站作者:玉研仪器
电子烟(electronic cigarette),是一种以电池供电的驱动雾化器,可加热雾化油舱中的电子液体(俗称烟油、电子果汁、e-liquid或e-juice;烟油含有1,2-丙二醇、植物甘油、食用香精或尼古丁)。虽然有研究表明长期吸食电子烟会导致气道炎症、嗜中性粒细胞增多、气道重塑和肺气肿(gotts et al, 2019),电子烟暴露可能导致dna损伤、氧化应激诱导的细胞死亡和核因子κb (nf-κb)介导的急性肺部炎症(gotts et al,2019;garcia-arcos et al,2016;ma et al,2021),但对电子烟各个成分对呼吸系统影响的研究较少,因此电子烟自问世以来一直备受争议。

2023年4月韩国毒理学研究所空气危险因素吸入毒理学中心sung-hoon yoon 等在journal of hazardous materials 杂志上发表了一篇名为comparative study of lung toxicity of e-cigarette ingredients to investigate e-cigarette or vaping product associated lung injury的文章,研究了电子烟产品中的尼古丁和四氢大麻酚等个别成分对呼吸系统的影响。实验中分别在小鼠气管内注射丙二醇(pg)、植物甘油(vg)、维生素e醋酸酯(vea)或尼古丁两周。在pg和vea处理的小鼠模型中发现了细胞学和组织学变化,这些小鼠表现出与电子烟使用相关肺损伤(evali)或电子烟使用者症状相关的病理生理变化。与潜在的人体暴露情况相比,虽然vea暴露条件与电子烟中vea含量的剂量当量相似,但pg条件约为电子烟使用者每日摄入pg剂量当量的47-137倍。这些结果表明,vea暴露比pg暴露更容易引起与evali相关的问题。转录组学分析显示,pg暴露通过akt信号通路和m2巨噬细胞极化与纤维化肺损伤相关,vea暴露通过丝裂原激活的蛋白激酶信号通路与哮喘性气道炎症相关。
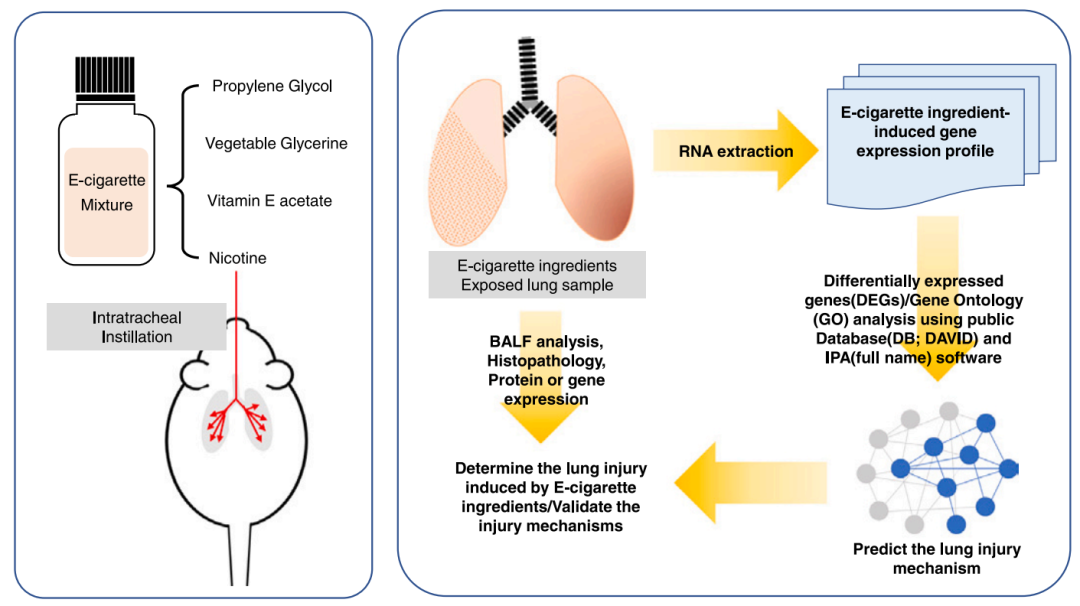
研究中,作者团队使用英国emms公司用力肺功能检测系统(espira™ forced manoeuvers system)对电子烟成分暴露小鼠各实验组进行肺功能检测,结果显示暴露于pg组小鼠通气功能显著减低(fev25/fvc和fev50/fvc);与对照组相比,pg和vea组小鼠的肺吸气量ic均有所增加;而pg组和vea组的呼气峰流量(pef)和肺吸气量(ic)则无显著差异。
lung function measurement. lung function measurement, including pef, fev25/fvc, and fev50/fvc following the groups of (a) pg or (b) vea exposure. the results are expressed as the mean for each group. # p<0.05 vs.each vehicle control.
英国emms公司是一家专注于肺功能研究领域的开发生产商,可提供最完善的呼吸功能研究测试仪器,并且在in-vivo,in-vitro,pulmonary,cardiovascular具有20多年以上相关技术经验。emms的产品已遍及国内外高校,药厂以及研究所,其中espira™用力肺功能检测系统是其最经典代表之一。
产品介绍
espira™用力肺功能检测系统(espira™ forced manoeuvers system)是emms用于检测与肺功能相关的全部生理数据的大型系统,可对麻醉动物进行一系列成组实验的数据自动分析检测,包括用力肺活量相关数据的测试。该系统可用于小鼠、大鼠/豚鼠以及其他大型动物。广泛应用于copd、广泛应用于慢阻肺、肺气肿、肺纤维化、矽肺、急性肺损伤、机械通气型肺损伤等各种急慢性呼吸系统疾病的临床前研究。
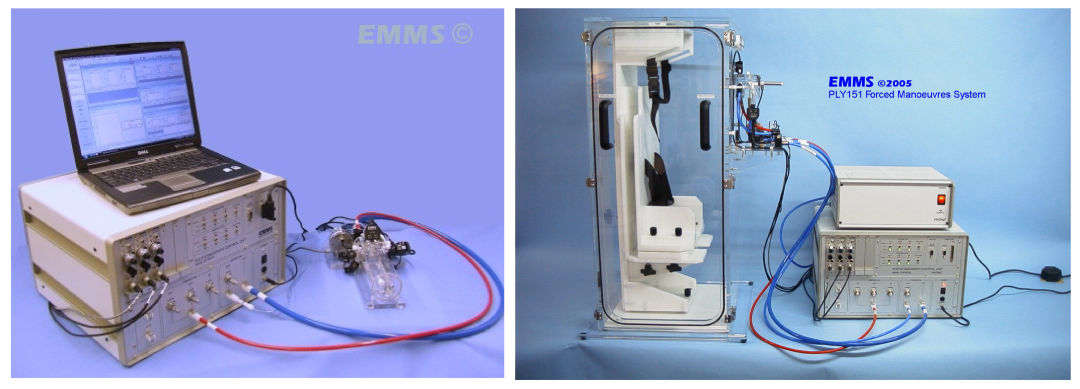
实验时,动物需麻醉并施以气管切开术。与人肺功能检测相类似,espira™系统提供与人类肺功能指标一致的各种生理指标参数。系统高度自动化并提供丰富的图标供分析研究使用,软件可自定义多种数据表格和图形形式,并可查看输出原始数据,并输出常用的 统计分析数据报告,还可以根据研究者实验需求灵活设置protocal,简化实验流程,提高实验效率,另有电子签名设置可保证实验数据的安全性和真实性,符合glp标准。
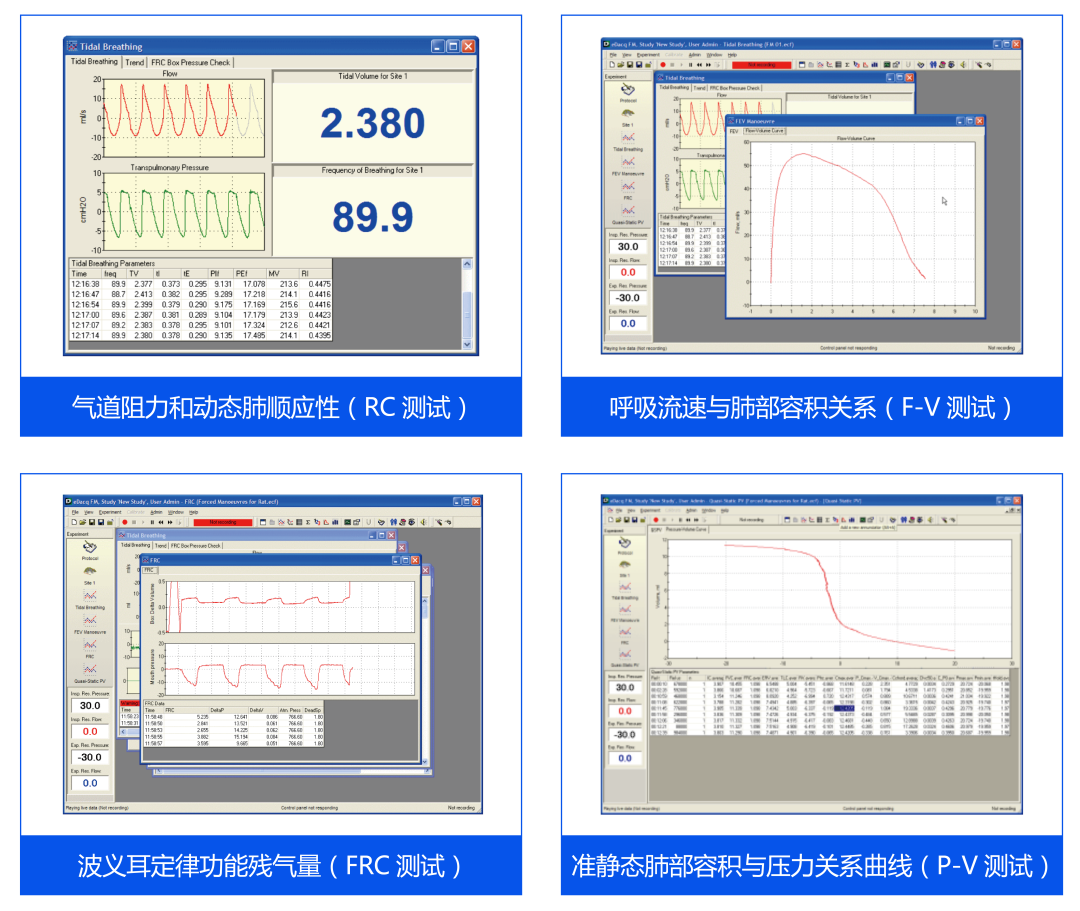
主要检测参数
(1)可检测参数包括但不限于:
用力呼气量 / forced expiratory volume (fev)
肺总量 / total lung capacity
用力肺活量 / forced vital capacity
最大呼气流量 / peak expiratory flow
最大呼气中段流量 / maximum mid expiratory flow
准静态压力容积曲线 / quasistatic pressure volume curves
功能残气量 / frc
阻力/顺应性 / resistance/compliance
(2)详细参数列表
| name | units | description |
| ic | ml | inspiratory capacity, volume inspired during slow inspiration |
| fvc | ml | forced vital capacity, volume expired during fast expiration |
| erv | ml | expiratory reserve volume, fvc-ic |
| fev25 | ml | volume expired in first 25 ms of fast expiration |
| fev50 | ml | volume expired in first 50 ms of fast expiration |
| fev75 | ml | volume expired in first 75 ms of fast expiration |
| fev100 | ml | volume expired in first 100 ms of fast expiration |
| fev200 | ml | volume expired in first 200 ms of fast expiration |
| fev400 | ml | volume expired in first 400 ms of fast expiration |
| fevpef | ml | volume expired at peak expiratory flow |
| ti | s | inspiration time |
| te | s | expiration time |
| pef | ml/s | peak expiratory flow |
| mmef | ml/s | mean mid expiratory flow, average flow between 25% - 75% fvc |
| fef75 | ml/s | forced expiratory flow at 75 % of fvc (25 % expired) |
| fef50 | ml/s | forced expiratory flow at 50 % of fvc |
| fef25 | ml/s | forced expiratory flow at 25 % of fvc (75 % expired) |
| fef10 | ml/s | forced expiratory flow at 10 % of fvc (90 % expired) |
| dvpef | % | % of fvc remaining at pef |
| holdtime | s | measured breath hold time |
| pinsp | cmh2o | pressure difference between start and end of inspiration |
| pexp | cmh2o | pressure difference between start and end of expiration |
| offset | ml/s | if the auto-detect zero flow level is enabled, this outputs the offset from calibrated flow zero to calculated flow zero. if zuto-zero detect is disabled, then this output is 0. |
| fevuser1 | ml | fev at user-defined output point 1. |
| fevuser2 | ml | fev at user-defined output point 2. |
| fevuser3 | ml | fev at user-defined output point 3. |
| fevuser4 | ml | fev at user-defined output point 4. |
| fevuser5 | ml | fev at user-defined output point 5. |
| frc | ml | functional residual capacity |
| deltap | cmh2o | pressure difference |
| deltav | ml | volume difference |
| pb | mmhg | barometric pressure, as set in control options |
| tol | % | percent tolerance between accepted breaths |
| deadsp | ml | amount of dead space, as set in manoeuvre options |
| ic | ml | inspiratory capacity, volume inspired during slow inspiration |
| fvc | ml | forced vital capacity, volume expired during fast expiration |
| frc | ml | functional residual capacity, as entered in manoeuvre options |
| erv | ml | expiratory reserve volume, fvc - ic |
| tlc | ml | total lung capacity, frc ic |
| rv | ml | residual volume |
| pfrc | cmh2o | pressure at frc |
| cmax | ml/cmh2o | maximum compliance |
| p_cmax | cmh2o | pressure at max compliance |
| v_cmax | ml | volume at max compliance |
| cchord | ml/cmh2o | chord compliance between 0-10 cmh2o |
| cfvc50 | ml/cmh2o | compliance at 50 % vc |
| c_p0 | ml/cmh2o | compliance at 0 pressure |
| pmax | cmh2o | max pressure |
| pmin | cmh2o | min pressure |
| thold | s | breath hold time |
产品特点
- espira™系统是copd、急性肺损伤、肺间质疾病等研究的必备工具,广泛适用于多种肺部疾病模型临床前研究
- 经典的肺量测定法(spirometry)检测frc功能残气量、fev、fvc用力肺活量、准静态肺顺应性、tlc肺总量、ic吸气能力、mmef平均呼气中期流量等直接生理数据,与人类医学肺功能检测的各种肺功能指标基本一致,是目前检测指标最完整的动物肺功能检测系统
- 适用于多种实验动物,内置金属正负压力储能器可适应更大压力范围,检测更大动物无需更换主机
- frc、f-v、p-v多个测试组合可在五分钟内完成并输出丰富的指标数据
- 可持续输出气道阻力rl、动态肺顺应性cdyn、潮气量等平静呼吸功能数据
- 检测跨肺压(胸腔内压)从而得到更精确的数据结果,排除呼吸机等的外部因素影响
- 检测中允许使用呼吸机和不使用呼吸机两种方式,标配为不使用呼吸机,以得到更真实的潮气量和呼吸频率等数据结果
- 主机内置小型计算机处理原始数据,数据采样率高达60khz
- 数据立即呈现,无须等待;多种图形及统计分析数据可供导出
- 数据传输和指令传达采用不同串口连线,避免了大量数据双向传输引起缓冲池溢出故障
- 可外接氧气、co、co2、氮气以及其它各种气体以满足多种实验方案
- 符合glp及fda final rule 21 cfr part 11相关标准
应用举例
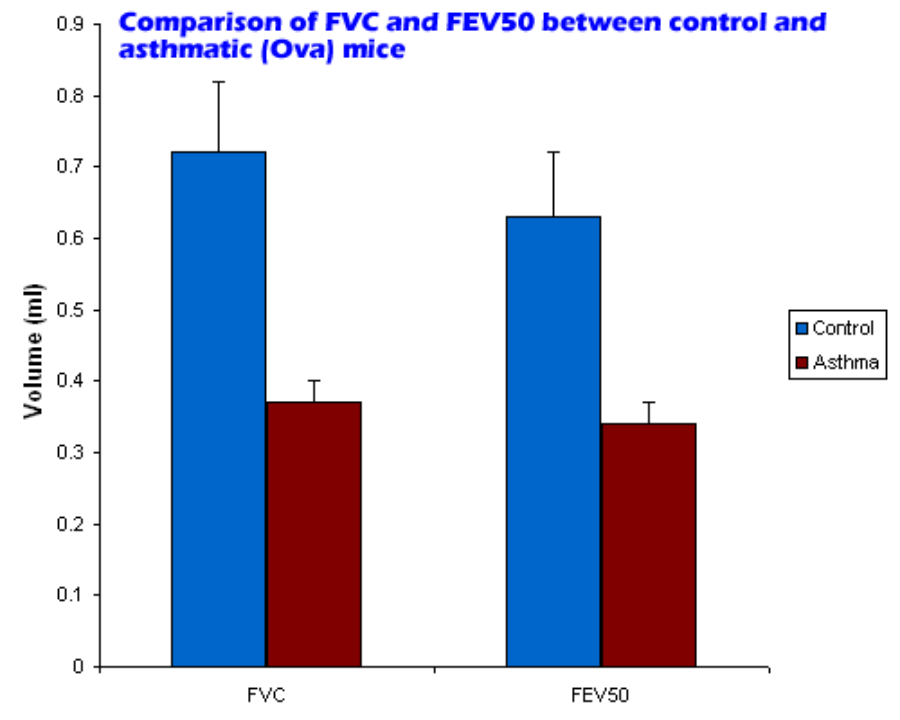
上图为利用espira™系统在慢性哮喘小鼠模型上获取的数据。小鼠通过卵清蛋白(ova)激发致敏,对照组只注射明矾和缓冲液。在最后一次激发24小时后进行肺功能检测。如图,fvc降低了49%,fev50降低了46%。数据表明espira™系统用于小鼠哮喘模型,可以有效的检测肺功能的改变。
参考文献
[1].yoon, s., et al., comparative study of lung toxicity of e-cigarette ingredients to investigate e-cigarette or vaping product associated lung injury. journal of hazardous materials, 2023. 445: p. 130454.
[2]. wang, j., et al., macrophage-derived gpnmb trapped by fibrotic extracellular matrix promotes pulmonary fibrosis. communications biology, 2023. 6(1): p. 136.
[3]. wang, m., et al., blockade of phosphotyrosine pathways suggesting sh2 superbinder as a novel therapy for pulmonary fibrosis. theranostics, 2022. 12(10): p. 4513.
[4]. li, q., et al., inhibition of rock ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing m2 macrophage polarisation through phosphorylation of stat3. clinical and translational medicine, 2022. 12(10): p. e1036.
[5]. seitz, a.m., et al., forces at the anterior meniscus attachments strongly increase under dynamic knee joint loading. the american journal of sports medicine, 2021. 49(4): p. 994-1004.
[6]. zhang, m., et al., quantitative evaluation of lung injury caused by pm2. 5 using hyperpolarized gas magnetic resonance. magnetic resonance in medicine, 2020. 84(2): p. 569-578.
[7]. chen, k., et al., early peritoneal dialysis ameliorates blast lung injury by alleviating pulmonary edema and inflammation. shock, 2020. 53(1): p. 95-102.
[8]. carrington, r., et al., c101 ipf: clinical studies, therapeutics, and more ii: nintedanib attenuates lung function decline in a bleomycin-induced rat model of pulmonary fibrosis. american journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 2017. 195.
[9]. chung, k.f., et al., inactivation, clearance, and functional effects of lung-instilled short and long silver nanowires in rats. acs nano, 2017. 11(3): p. 2652-2664.
[10].klar, j., et al., fibroblast growth factor 10 haploinsufficiency causes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. journal of medical genetics, 2011. 48(10): p. 705-709.
您想了解更多详细资料吗?
请与我们联系:
tel:021-35183767,021-54377179
18502129044
qq:3007536034
微信:yuyanbio
mail:yuyanbio@126.com
欢迎您的咨询!
